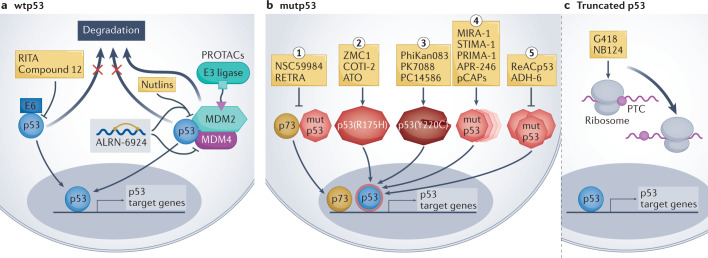
Fig. 3. p53-based small molecules for cancer therapy.
a | In p53-wild-type (wtp53) tumours, small-molecule drug development is mainly focused on inhibiting or degrading negative regulators of p53, including MDM2, MDM4 and human papillomavirus (HPV) E6. Such inhibition increases p53 protein abundance and wtp53 activity in the cancer cells, promoting the expression of p53 target genes. ALRN-6924 is a stapled peptide that blocks both MDM2–p53 and MDM4–p53 interactions. p53-activating proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) work by targeting MDM2 for ubiquitylation by particular E3 ligases, resulting in MDM2 degradation. b | In tumours expressing missense mutant p53 (mutp53) proteins, drug development aims to restore wtp53 conformation and/or inhibit gain-of-function activities of mutp53 such as inhibition of p73. From left to right: (1) small molecules such as RETRA (reactivation of transcriptional reporter activity) or NSC59984, which inhibit the interaction of mutp53 with p73, unleash p73 and enable it to enter the nucleus and transactivate target genes that partly overlap with p53 target genes. (2) Some small molecules (arsenic trioxide (ATO), ZMC1) act predominantly on structural p53 mutants (such as p53(R175H)) to restore wtp53 conformation and induce p53 target gene expression. (3) The p53(Y220C) mutant has an accessible crevice near the site of mutation, which can be targeted by small molecules to thermodynamically stabilize the mutant protein and shift it towards a wild-type-like state. (4) Many compounds (such as APR-246 and pCAPs) target a broad spectrum of p53 mutants to restore a wtp53-like structure, thus enabling p53 target gene activation (for a more detailed mechanistic description see ref.195). (5) Some small molecules — such as ReACp53 or ADH-6 — act by inhibiting mutp53 aggregation, restoring wtp53-like structure and activating p53 target genes. c | Other small molecules inhibit the recognition of premature termination codons (PTCs), enabling translational readthrough and synthesis of full-length p53 protein in cells that harbour truncating TP53 mutations. The overarching goal of all these drugs is to restore the expression of wtp53 target genes as a means to induce cancer cell death or replicative senescence, thereby curtailing tumour growth. RITA, reactivation of p53 and induction of tumour cell apoptosis.