Figure 2.
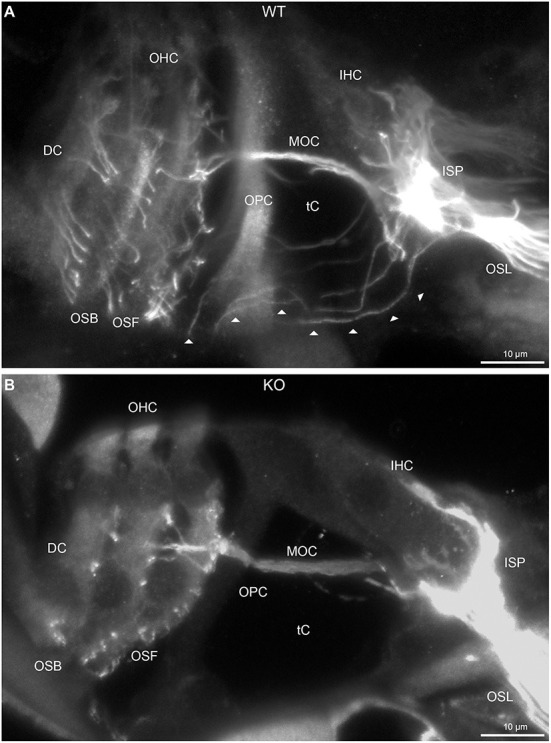
Disruption of type II spiral ganglion afferents, the outer spiral fibers (OSF), in the mid-basal region of the Prph knockout (KO) delineated using β-III tubulin immunofluorescence. (A) In the WT cochlea, the type II spiral ganglion afferents exit from the basal aspect of the inner spiral plexus (ISP) beneath the inner hair cells (IHC), cross the floor of the tunnel of Corti (tC) (arrowheads), pass between the outer pillar cells (OPC) and turn basally to form parallel sheets of OSF along the sides of the Deiters' cells (DC), as the outer spiral bundles (OSB). The OSF branch periodically and turn apically to terminate along the three rows of outer hair cells (OHC). The medial olivocochlear (MOC) efferent fibers cross the mid-region of the tC to innervate the OHC. (B) In the PrphKO image, the OSF density is substantially reduced, while equivalent MOC efferent fiber projections extend to the OHC. OSL, osseous spiral lamina. Transparent-mode confocal reconstructed images of batch-processed WT and PrphKO cryosections; 21–25 μm depth z stacks. See also Supplementary material 2.
