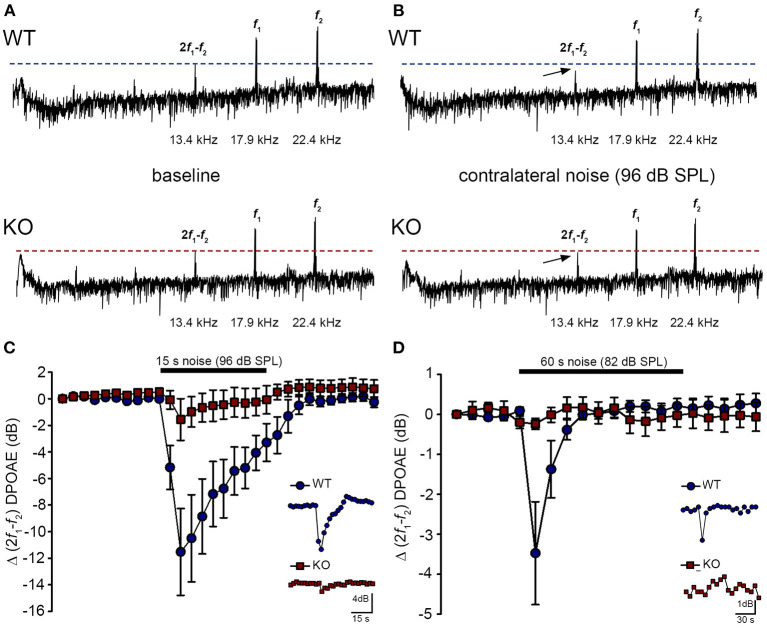
Figure 7.
Contralateral suppression (CS) of the cubic (2f1-f2) DPOAE in wildtype (WT) and PrphKO mice under ketamine/xylazine/acepromazine anesthesia. (A,B), Examples of fast Fourier transforms of the DPOAE in the frequency domain with WT and KO at baseline (A,B) with the presentation of contralateral noise (96 dB SPL, 15–25 kHz, 15 s duration, with f1 and f2 about 20 kHz using 60 dB SPL drivers). The cubic DPOAE (arrows) is diminished in the WT mouse (contralateral suppression) but is not affected in the KO mouse. (C) Data showing the difference in contralateral suppression with presentation of 96 dB SPL white noise in the WT mice and KO mice. Note the rapid onset to peak contralateral suppression at ~ 3 s, followed by almost complete adaptation by 15 s (unpaired t-test; n = 7 per group). (D) Difference in contralateral suppression between WT and KO mice during 82 dB SPL noise (60 s, about 10–17 kHz, with f1 and f2 about 28 kHz using 65 dB SPL drivers). Note the complete adaptation by ~30 s in the WT mice, whereas the DPOAE is unchanged in the KO mice (unpaired t-test; n = 8 per group).