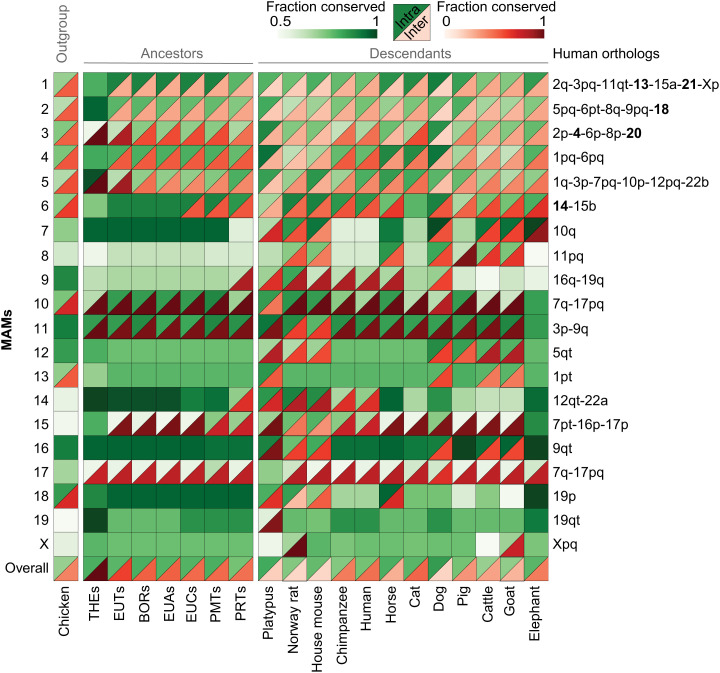
Fig. 3.
Visualization of the evolutionary history of reconstructed mammalian chromosomes based on the human lineage. Solid green squares indicate mammalian chromosomes maintained as a single synteny block (either as a single chromosome or fused with another MAM), with shades of the color indicating the fraction of the chromosome affected by intrachromosomal rearrangements (the lightest shade is most affected). Split blocks demarcate mammalian chromosomes affected by interchromosomal rearrangements. Upper (green) triangles show the fraction of the chromosome affected by intrachromosomal rearrangements, and lower (red) triangles show the fraction affected by interchromosomal rearrangements. Syntenic relationships of each MAM to the human genome are given at the right of the diagram. MAMX appears split in goat because its X chromosome is assembled as two separate fragments. BOR, boreoeutherian ancestor chromosome; EUA, Euarchontoglires ancestor chromosome; EUC, Euarchonta ancestor chromosome; EUT, eutherian ancestor chromosome; PMT; Primatomorpha ancestor chromosome; PRT, primates (Hominidae) ancestor chromosome; THE, therian ancestor chromosome.