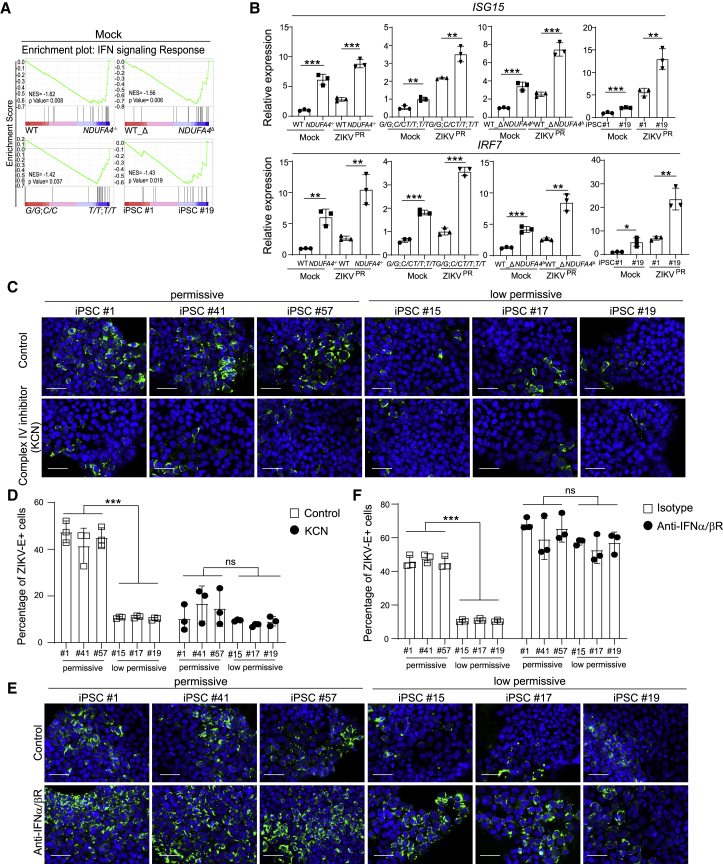
Figure 7.
Loss or reduction of NDUFA4 triggers type I interferon signaling
(A) Gene Set Enrichment Analysis of type I interferon signal pathway in 4 groups of hiPSCs. 4 groups: WT versus NDUFA4−/−, risk (G/G; C/C) versus non-risk (T/T; T/T), WT_Δ versus NDUFA4Δ, and iPSC #1 versus iPSC #19.
(B) qRT-PCR analysis of ISG15 and IRF7 mRNA expression levels with mock or ZIKV infection at 72 hpi (ZIKVPR, MOI = 1). 4 groups: WT versus NDUFA4−/−, risk (G/G; C/C) versus non-risk (T/T; T/T), WT_Δ versus NDUFA4Δ, and iPSC #1 versus iPSC #19. The value was normalized to ACTB.
(C and D) Representative confocal images (C) and the quantification (D) of ZIKV-E staining of permissive cell lines iPSC #1, iPSC #41, and iPSC #57 and low-permissive cell lines iPSC #15, iPSC #17, and iPSC #19 treated with potassium cyanide (KCN) at 72 hpi (ZIKVPR, MOI = 1). Scale bar, 50 μm.
(E and F) Representative confocal images (E) and the quantification (F) of ZIKV-E staining of permissive cell lines iPSC #1, iPSC #41, and iPSC #57 and low-permissive cell lines: iPSC #15, iPSC #17, and iPSC #19 treated with blocking antibodies of IFNAR at 72 hpi (ZIKVPR, MOI = 1). Scale bar, 50 μm.
Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data are shown as mean ± SD. p values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S7.