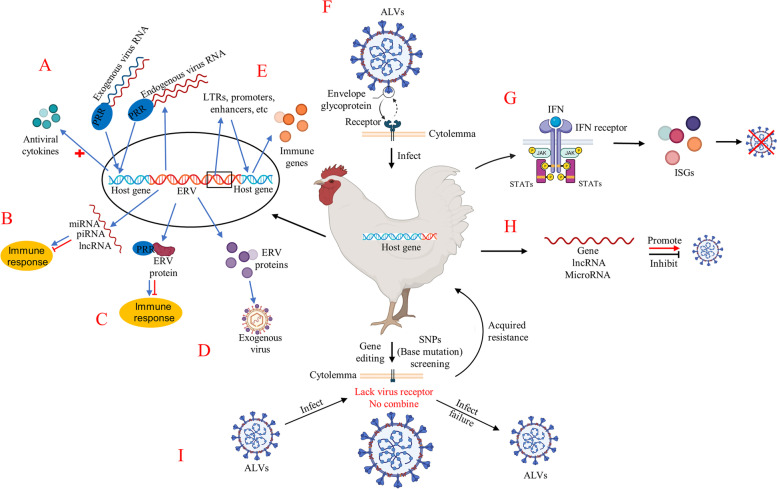
Fig. 1.
Host genes and genomes are closely related to avian leukosis virus (ALV) resistance. A Nucleic acids derived from ERVs can be considered as a type of pattern recognition receptors, which can recognize its complementary exogenous viral RNA and trigger a more specific immune response; B Small RNA molecules derived from ERVs, such as miRNA, piRNA, and lncRNA, can modulate the antiviral immune response in a direct manner; C ERVs-derived proteins modulate the antiviral immune response; D ERVs-derived proteins interfere with the receptors of exogenous viruses; E The retroviral elements of ERVs regulate host immune gene expression; F ALV invades the host by binding to the receptors on the host cell membrane; G IFNs bind their cognate receptors to induce ISGs through the JAK/STAT pathway after ALV infection; H Immune-related factors in the host genome can promote or inhibit virus replication after ALV infection; I Using gene editing methods to knock out the viral receptor gene or screen individuals with mutations in viral receptor gene, there is no viral receptor on the host cell membrane, ALV cannot bind to the receptor and infect the host, and the host will also acquire resistant to ALV