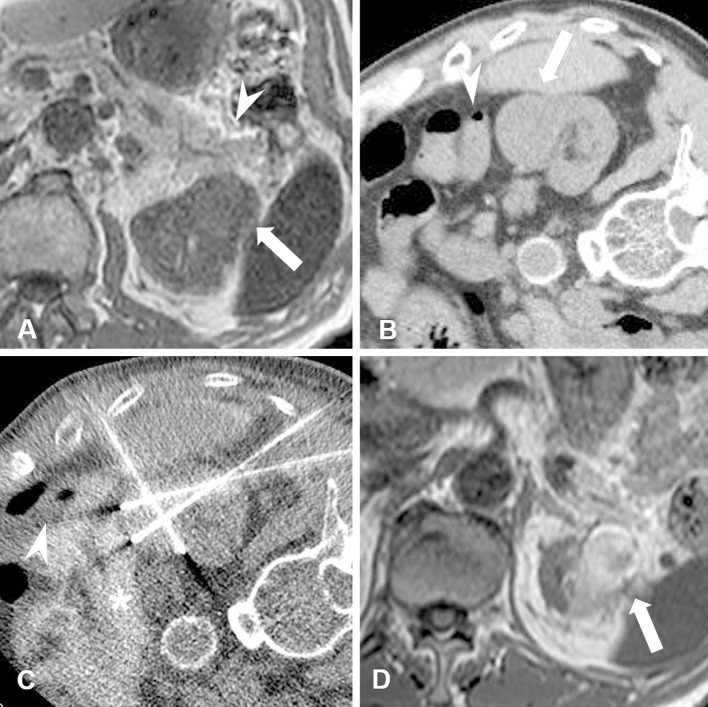
Figure 2.
A male patient in his 70s with chronic kidney disease (estimated GFR: 21.7). Biopsy-proven RCC (maximum tumor diameter, 3.2 cm) is seen in the left kidney. A. Non-contrast-enhanced MRI T1-weighted scan shows RCC (arrow) adjacent to the pancreas (arrowhead). B. CT image obtained in the right lateral decubitus position (ablation-side up). In this position, the pancreas is positioned away from the RCC but the colon (arrowhead) is adjacent to the tumor (arrow). C. CT image obtained during RF ablation shows the colon (arrowhead) dislocated using hydrodissection fluid (asterisk). Iodinated contrast medium was mixed in with the hydrodissection fluid. D. Non-contrast-enhanced MRI T1-weighted scan obtained at six months after RF ablation shows shrinkage of the ablated RCC (arrow) and no thermal damage to surrounding organs.