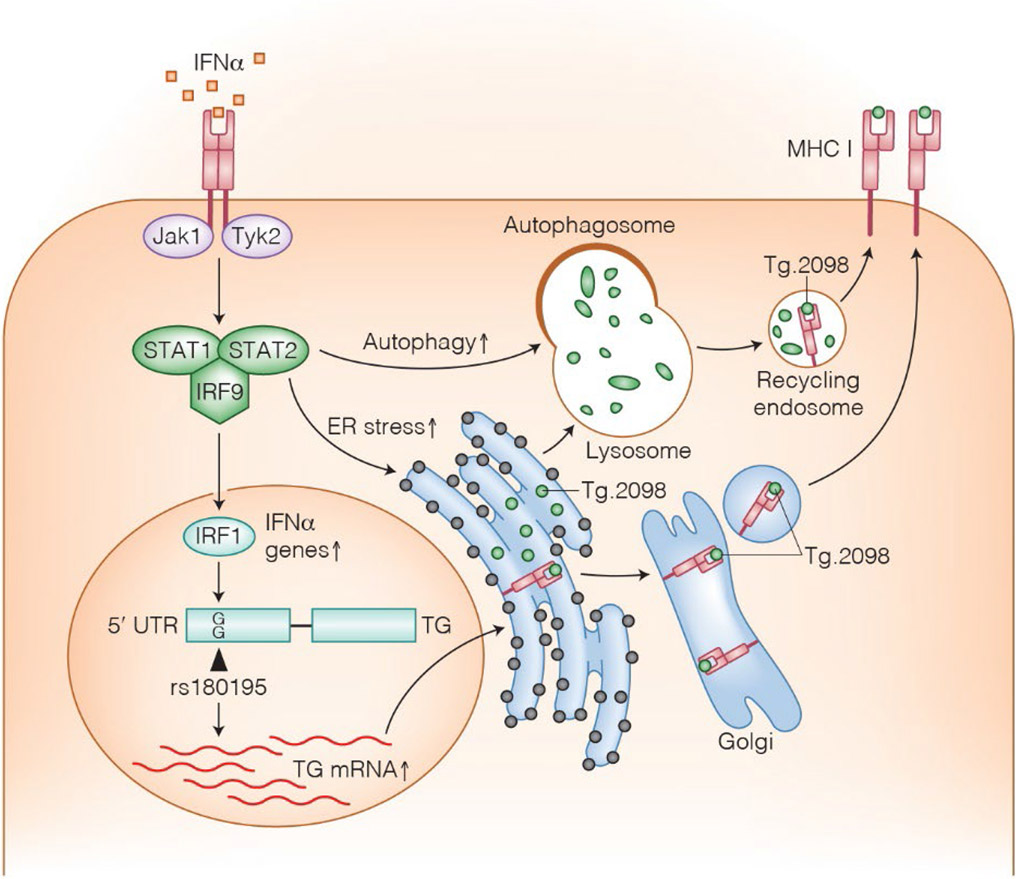
Figure 1:
A proposed model for environmental-genetic interaction leading to anti-Tg autoimmunity. Viral infections lead to local secretion of IFNα which in turn binds to its receptor on thyroid cells and on immune cells. Immune cell binding leads to secretion of chemokines and recruitment of immune cells. Thyroid cell binding triggers increased synthesis of Tg, as well as ER stress and increased autophagy within thyroid cells. Both lead to Tg degradation into immunogenic peptides, such as Tg.2098 that can be presented to immune cells.