Fig. 1 |. Generation of a syngeneic mouse model of DIPG.
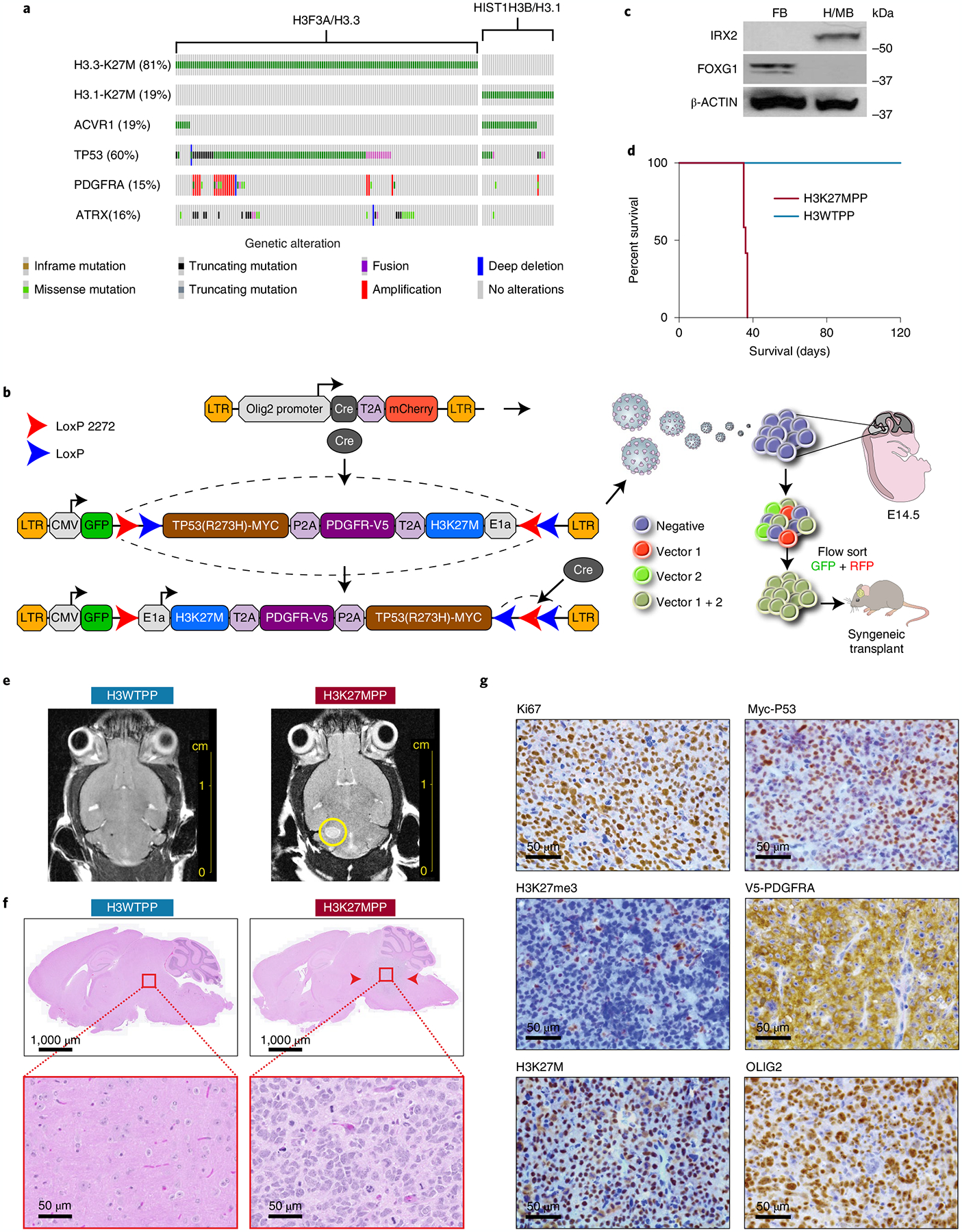
a, Oncoprint of H3K27M mutant tumors with top alterations. In addition to H3K27M, we selected PDGFRA and TP53 to target in our model development. b, Schematic of strategy used to target OLIG2-positive NPCs using flip-excision (FLEx) cassette switches, whereby Olig2 promoter drives Cre expression and the target genes H3F3A, TP53 and PDGFRA are inverted. c, Western blot confirming regional isolation of NPCs. FOXG1 for forebrain and IRX2 for mid/hindbrain. All western blots were performed in biological triplicate. d, Kaplan–Meier survival curve of 2.5 × 104 H3K27MPP cells or H3WTPP cell injected into the midbrain-pons of immunocompetent C57BL/6 mice. A log-rank Mantel–Cox test was performed between the groups with n = 12 mice per group (6 male and 6 female). ****P = 0.0005. e, MRI viewing the axial plane of mice 14 d after injection confirming tumor in H3K27MPP cells. f, Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining confirming high-grade glioma histology from H3K27MPP-injected cells. g, Immunohistochemistry confirming transgene expression in vivo and loss of H3K27me3 in our model. All experiments were performed in biological triplicate.
