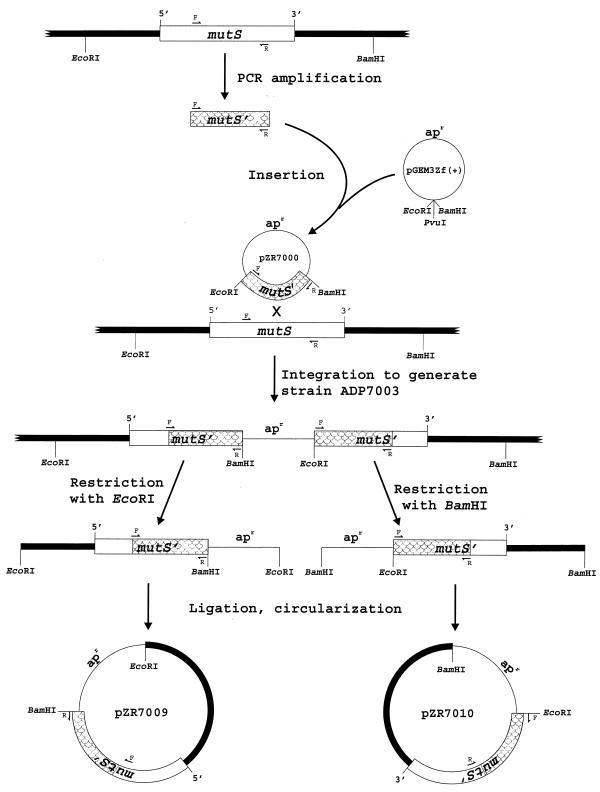
FIG. 1.
Cloning of mutS and flanking DNA from the chromosome of Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1. Small arrows indicate the degenerate primers MUTSF2 (F) and MUTSR3 (R) used for PCR amplification of a 1.9-kb segment of mutS. Shaded regions indicate this portion of mutS throughout the figure. Strain ADP7003 was formed by integration of pZR7000 into the chromosome of strain ADP1. pGEM-3Zf(+) does not replicate in strain ADP1, so selection for ampicillin resistance (apr), encoded on the vector, demanded strain ADP7003. Digestion of chromosomal DNA from strain ADP7003 with EcoRI yielded a fragment containing pGEM-3Zf(+) fused to a segment of upstream DNA that included the 5′ end of mutS, and chromosomal DNA extending to the first EcoRI site upstream of the gene. Circularization of the restriction fragments by ligation followed by transformation into E. coli DH5α and selection for Apr resulted in pZR7009. The 3′ end of mutS and downstream DNA were cloned in the same manner except that ADP7003 DNA was digested with BamHI rather than EcoRI, and the resulting plasmid was designated pZR1010.