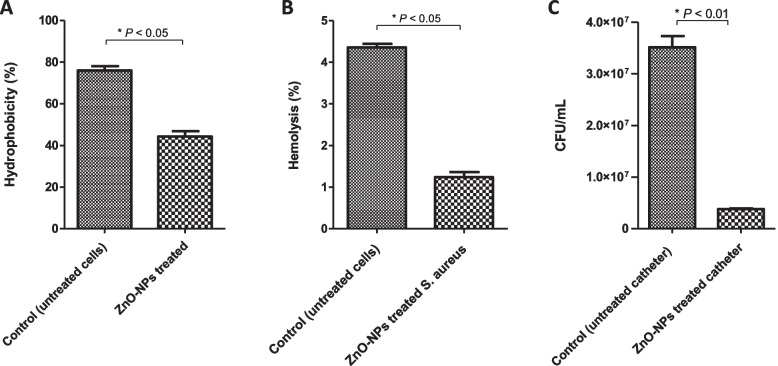
Fig. 5.
A ZnO-NPs reduced hydrophobicity index of S. aureus. Bacterial cells were grown overnight in presence and absence of ZnO-NPs. Bacterial density adjusted to 1.0 ± 0.01, then 1 ml of toluene was added to bacterial suspension. After that optical density of aqueous phase was measured. B ZnO-NPs inhibited S. aureus-induced haemolysis. RBCs were incubated with S. aureus alone (control) or S. aureus treated with ZnO-NPs. Percentages of haemolysis were measured. C ZnO-NPs decreased S. aureus biofilm formation on urinary catheter. Catheter segments were immersed in S. aureus culture in presence or absence of sub-MIC of ZnO-NPs. Following incubation for 48 h, bacterial counts on the surface of catheter were determined after serial dilution in PBS and plating on mannitol salt agar. The total number of biofilm cells of ZnO-NPs treated catheters was significantly (*P < 0.05) less than untreated catheter. All results are expressed as means ± SE of three independent experiments using Student’s t test