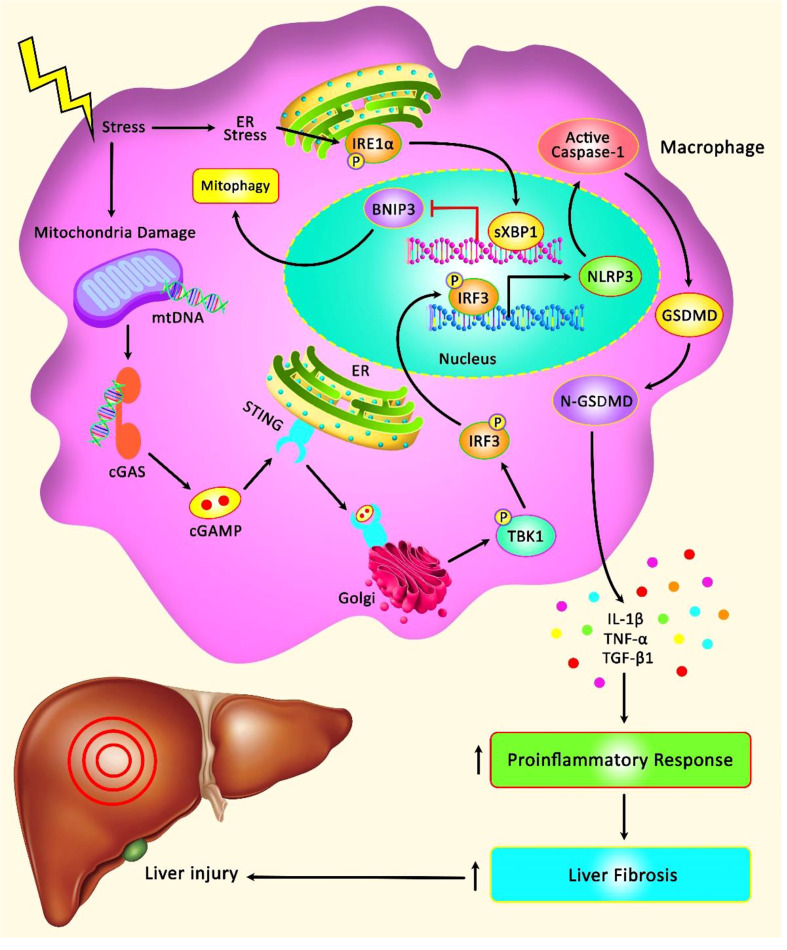
Figure 1.
A schematic illustration of the role of NLRP3 Inflammasome involved in the hepatic I/R injury. Mounting evidence has detected that STING/TBK1/NLRP3 signaling cascade can play a remarkable role in modulating innate immune activation and promoting liver IR injury in aged mice. STING can regulate the activation of NLRP3 signaling and excessive secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in the mtDNA-stimulated bone marrow-derived macrophages from aged mice. Moreover, STING upregulation in macrophages can elevate the detrimental role of aging in aggravating liver IR injury and intrahepatic inflammation (12). Furthermore, another research has illustrated that XBP1 can regulate macrophage cGAS/STING/NLRP3 activation via elevating macrophage self-mtDNA cytosolic leakage in liver fibrosis. Therefore, macrophage self-mtDNA can play an effective role as an intrinsic trigger for macrophage cGAS/STING activation that can be modulated through regulating XBP1/mitophagy (13).