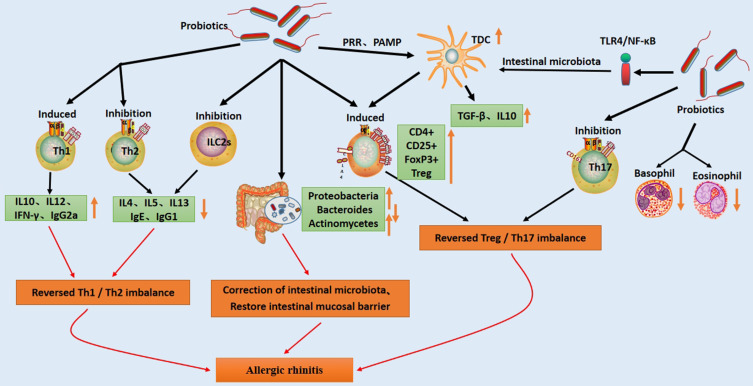
Figure 2.
Brief mechanism of probiotic treatment of allergic rhinitis. Probiotics protect against allergic rhinitis by reducing serum pro-inflammatory factors, increasing the number of immune cells, regulating Th1 and Th2 balance, increasing Treg numbers, and inhibiting Th17. In addition, probiotics can directly stimulate the formation of TDCs or activate the TLR pathway to indirectly stimulate DC, thereby inducing the formation of Tregs. Probiotics can improve AR by increasing the level of beneficial bacteria to regulate the stability of the gut microbiota, restoring the intestinal mucosal barrier.
Abbreviations: TDC, tolerogenic dendritic cell; IL, interleukin; ILC2s, type 2 innate lymphocytes; IgE, immunoglobulin E; IgG2a, immunoglobulin G2a; IgG1, immunoglobulin G1; Th1, type 1 helper T lymphocyte; Th2, type 2 helper T lymphocyte; Th17, type 17 helper T lymphocyte; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; TLR4/NF-κB, toll like receptor-4/nuclear factor-κB; Foxp3, forkhead box protein p3; Treg, T regulatory cells.