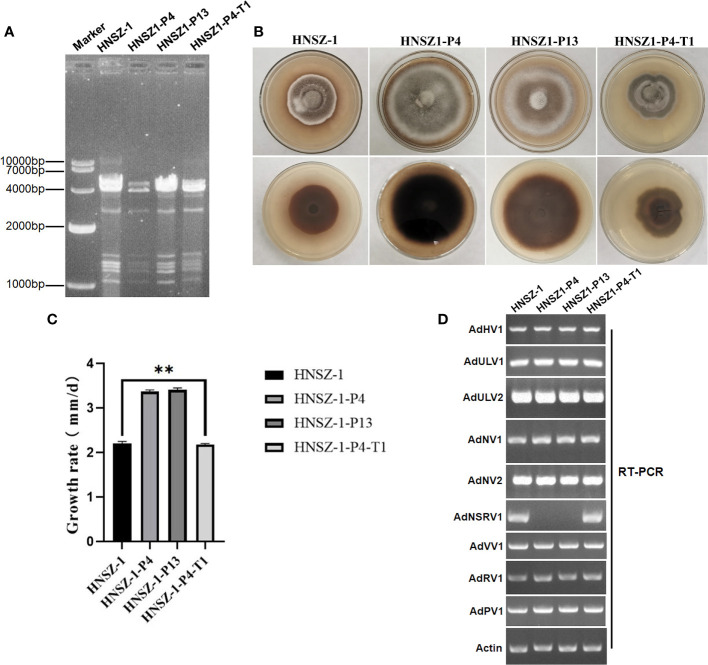
Figure 7.
Mycovirus content and biological features of strain HNSZ-1 and other derivative strains. (A) Detection of viruses in strain HNSZ-1, its protoplast regeneration derivatives HNSZ-1-P4 and HNSZ-1-P13, and the re-infected derivative strain HNSZ1-P4-T1 by dsRNA extraction. Strain HNSZ-1 and HNSZ1-P4-T1were the original and re-infected strains, respectively, that were co-infected by all the nine viruses. Strains HNSZ-P4 and HNSZ-1-P13 were detected to lack the AdNSRV1. (B, C) Colony morphology (B) and growth rate ** means significant difference at P < 0.05. (C) of strain HNSZ-1, the two protoplast regeneration derivatives HNSZ-1-P4 and HNSZ-1-P13, and the re-infected strain HNSZ1-P4-T1. (D) Detection of viruses in strain HNSZ-1, its protoplast regeneration derivatives HNSZ-1-P4 and HNSZ-1-P13, and the re-infected strain HNSZ1-P4-T1 by RT-PCR. Strain HNSZ-1 was the original strain co-infected by nine viruses, while strains HNSZ-P4 and HNSZ-1-P13 were detected to lack the AdNSRV1. Strain HNSZ1-P4-T1 was a derivative strain of HNSZ1-P4 obtained by virus horizontal transmission experiment, that was re-infected by nine viruses including AdNSRV1.