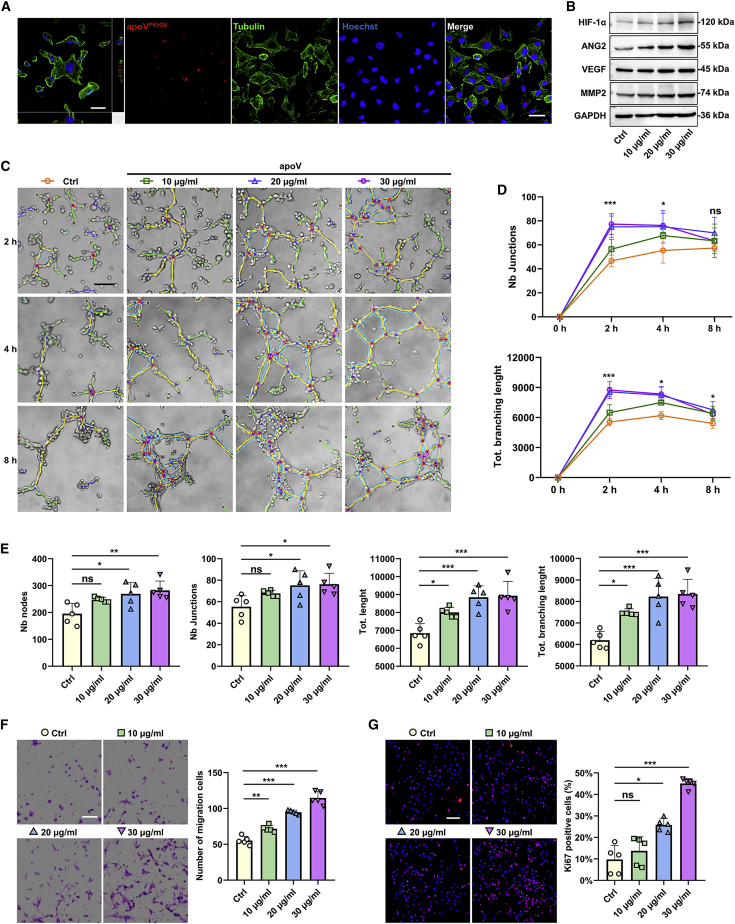
Figure 4.
hDPSC-apoVs enhance the angiogenic capacity of the ECs
(A) Representative confocal orthogonal view shows the uptake of PKH26-labeled apoVs (red) by ECs (green), counterstained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) Western blot analysis shows the expressions of HIF-1α, VEGF, ANG2, and MMP2 in ECs after incubation with apoVs at concentrations of 10, 20, or 30 μg/mL for 12 h. (C–E) Matrigel analysis shows the effect of hDPSC-apoVs on tube formation capacity of ECs. Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) ∗Comparison between Ctrl and 20 μg/mL, (E) ∗compared with Ctrl. (F) Transwell assay shows the effect of hDPSC-apoVs on migration capacity of ECs. Scale bar, 100 μm. (G) Immunofluorescent staining of MKI67 shows the effect of hDPSC-apoVs on the proliferation capacity of ECs. Scale bar, 100 μm; n = 5 per group. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analyses were performed by Student’s t test (two-tailed) or Student’s t test with Welch correction (two-tailed) for two-group comparisons and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test or Welch’s ANOVA with Games-Howell post hoc test for multiple-group comparisons. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ns, p > 0.05.