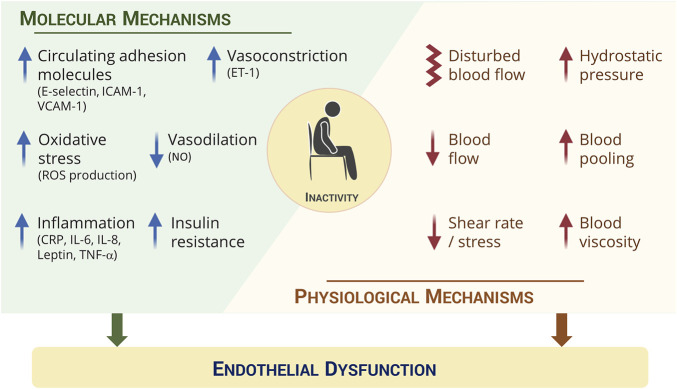
FIGURE 2.
Proposed underpinning mechanisms by which physical inactivity induces endothelial dysfunction in humans include modulation of i) molecular components associated with vasodilation/vasoconstriction, vascular adhesion, inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin resistance, as well as ii) physiological components, mainly in the lower limbs, such as declines in blood flow and shear stress/rate and increases in hydrostatic pressure, blood pooling and viscosity. CRP: C-reactive protein; ET-1: Endothelin-1; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-8: Interleukin-8; NO: Nitric oxide; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1.