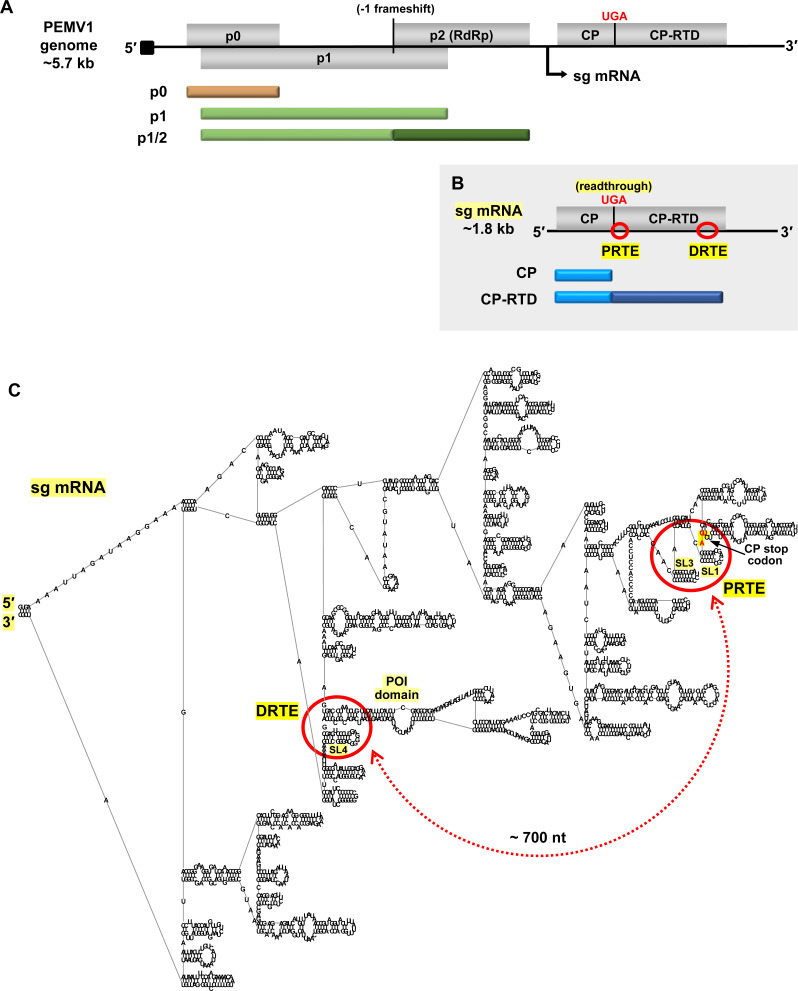
Fig 1. Organization of PEMV1 genome and subgenomic mRNA.
(A) Linear representation of PEMV1 genome showing encoded ORFs (grey boxes) for p0, p1, p2, coat protein (CP) and coat protein-readthrough domain (CP-RTD). Proteins translated from the genome are shown beneath it as tan and green bars. P1/2 RdRp protein is expressed via programmed -1 frameshifting within the p1 ORF. Black arrow beneath the genome indicates the transcription initiation site for the subgenomic (sg) mRNA. The black square at the 5′-end of the genome represents the VPg. (B) PEMV1 sg mRNA encoding CP and CP-RTD. Corresponding translation products are indicated below as blue bars. CP-RTD is expressed via programmed readthrough of the CP UGA stop codon. Relative positions of the proposed readthrough-regulating proximal readthrough element (PRTE) and distal readthrough element (DRTE) are shown as red circles. (C) RNA secondary structure model of full-length PEMV1 sg mRNA, as predicted by RNAStructure using default settings [34] and rendered using RNA2Drawer [57]. Labelled are the 5′ and 3′ ends, PRTE, DRTE, CP stop codon, SL1, SL3, SL4 and the pink-orange intervening (POI) domain. The red circles on the folded structure correspond to the regions circled on the linear sg mRNA in panel B. The proposed long-distance RNA-mediated interaction between PRTE and DRTE is indicated by a red double-headed arrow, and spans approximately 700 nt.