FIGURE 2.
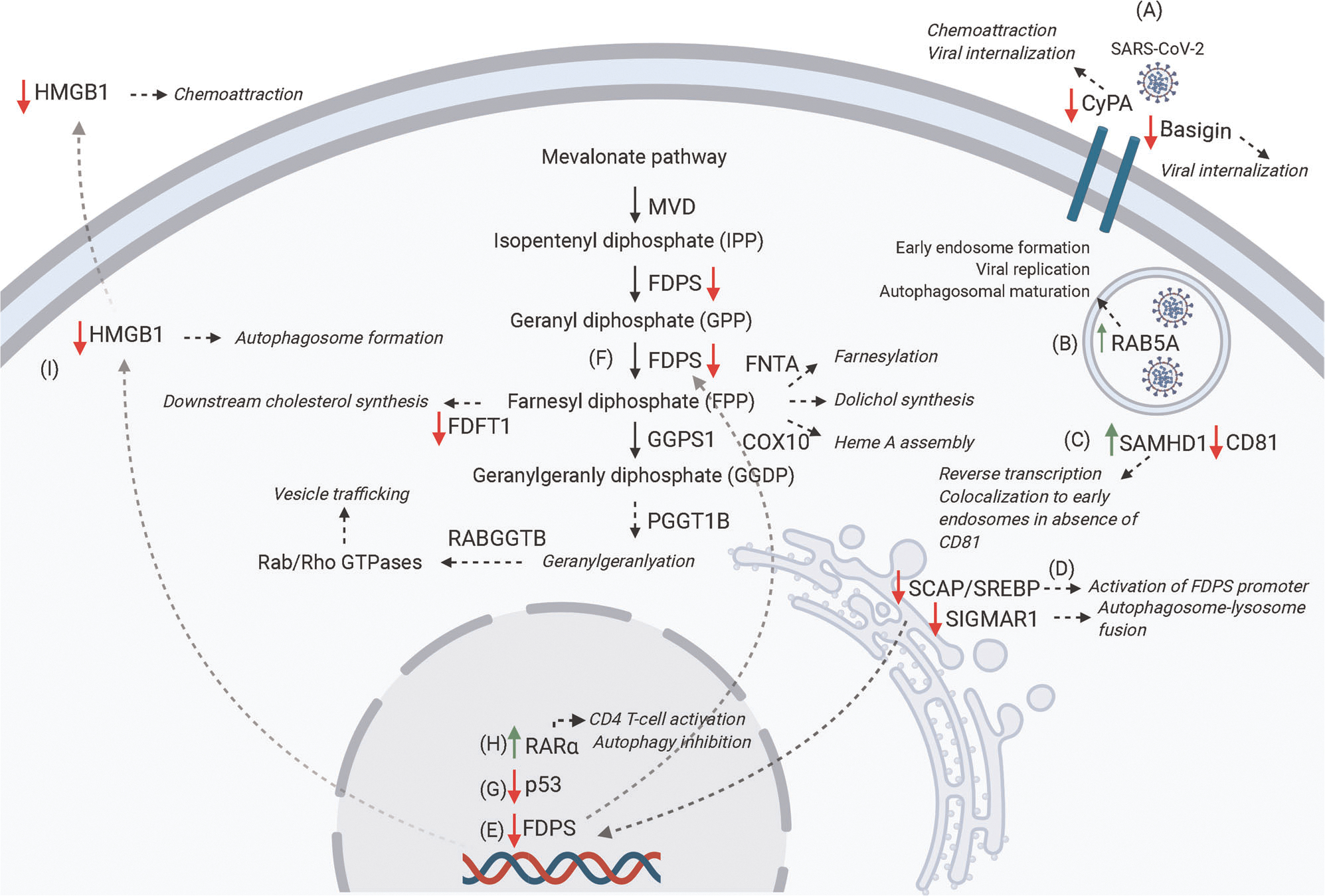
Schematic representation of proposed genes involved in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis based on GSE147507. (A) SARS-CoV-2 infection promotes downregulation of the membrane receptors CyPA and Basigin, both of which are involved in viral internalization. CyPA also contributes to chemotaxis. (B) SARS-CoV-2 upregulates Rab5A, which is involved in early endosome formation, viral replication, and autophagosomal maturation. (C) SARS-CoV-2 upregulates SAMHD1, which colocalizes to endosomes when CD81 expression is decreased. SAMHD1 is also involved in the reverse transcription of HIV. (D) SARS-CoV-2 downregulates SCAP/SREBP, which modulates the mevalonate pathway through activation of FDPS promoter (E). SARS-CoV-2 downregulates FDPS and FDFT1. These genes are involved in downstream geranyl/farnesylation and cholesterol synthesis, respectively (F). SARS-CoV-2 downregulates p53, which helps in preventing SARS-CoV replication (G). SARS-CoV-2 upregulates RAR-α, which is involved in CD4 T-cell activation and autophagy inhibition (H). SARS-CoV-2 downregulates HMGB1, which promotes autophagosome formation when present in the cytoplasm and has chemotactic activity when released extracellularly (I) (figure created with BioRender.com)
