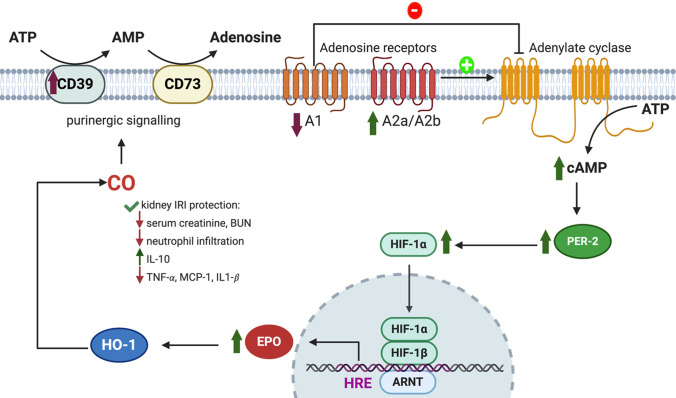
Fig. 25.
During tissue hypoxia, the upregulated ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73 convert extracellular ATP to adenosine as an adaptive response. Adenosine activates adenosine receptors, including A1 and A2a/A2b, which differentially act on the adenylate cyclase. Activation of A1 inhibits adenylate cyclase through coupled inhibitory G protein, whereas activation of A2a/A2b stimulates adenylate cyclase to generate cAMP from ATP. CO is protective in mouse models of kidney IRI through upregulation of CD39 ectonucleotidase expression, decreasing A1 expression, and increasing A2 expression, which lead to cAMP-mediated stabilization of Per2 and HIF-1α and upregulation of EPO gene transcription. A feed-forward loop is postulated, wherein EPO stimulates expression of HO-1, which can further increase CO through heme degradation.