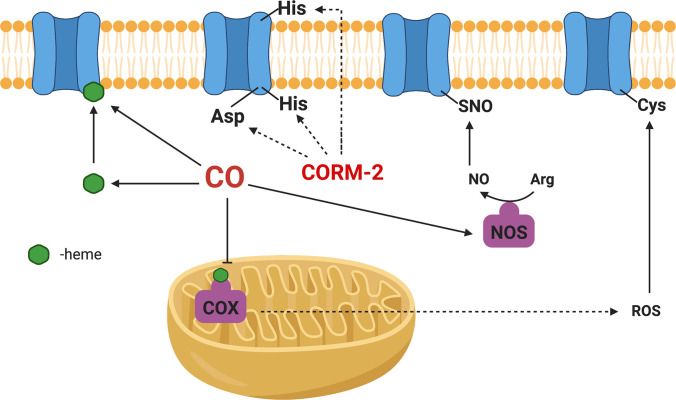
Fig. 26.
Possible molecular mechanisms for the actions of CO and CORM-2 on ion channels. CO released from CORM-2 binds to heme-containing ion channels through two possible mechanisms: 1) direct binding to the heme prosthetic group in the ion channel and 2) binding to the free heme first before engaging the ion channel. CO binding modulates the function of ion channel; CO inhibits COX, thus increasing intracellular ROS production, which acts on redox-sensitive ion channels; CO interacts with NOS, thus affecting NO production, leading to direct modulation of NO-sensitive ion channels or through a second messenger pathway to regulate ion channels; CORM-2 itself exhibits CO-independent activities on ion channels as well.