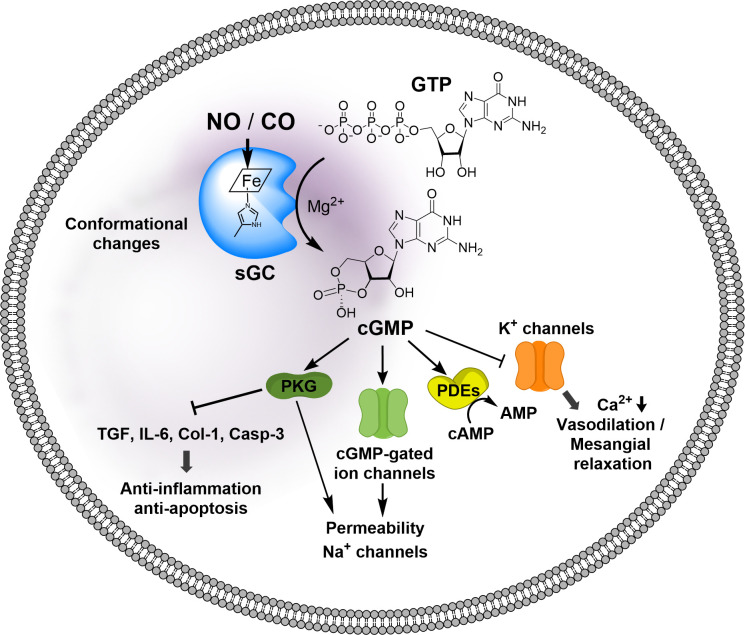
Fig. 9.
NO/cGMP signaling pathways. NO or CO binding to the heme prosthetic group induces conformational changes of the catalytic domain, thus increasing the catalytic activity to produce cGMP from GTP. cGMP as a second messenger binds to intracellular target proteins; activation of protein kinase G inhibits expression of profibrotic genes, including transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), Type-I collagen (Col-1), proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6), activation of proapoptotic protein Caspase 3 (Casp-3), activation of cGMP-gated ion channels, activation of phosphodiesterases (PDEs), and inhibition of K+ channels, thus decreasing intracellular Ca2+ concentrations.