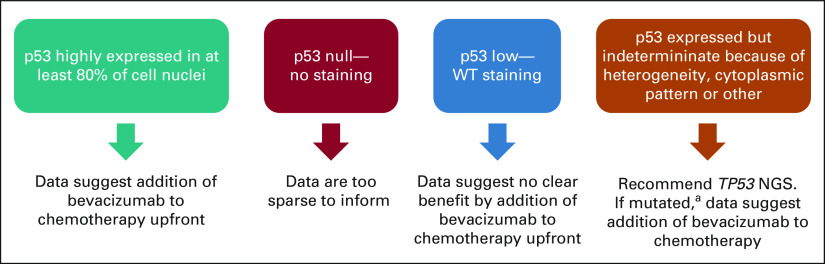
FIG 5.
A potential clinical management schema supported by the findings from GOG-86P. For ease and feasibility, tumor testing for p53 status can begin with standard IHC. If p53 is highly expressed in the nuclei of 80% of more of tumor cells, our data indicate that bevacizumab, when added to chemotherapy in the upfront setting, significantly improves PFS and OS. If the immunostaining is negative entirely, or null, we cannot make a strong recommendation because of the low number of cases, but we are aware that some p53 null cases appeared to benefit on the bevacizumab arms of GOG-86P. Therefore, we recommend weighing the risk of bevacizumab, including hypertensive complications, in each individual patient before adding bevacizumab to upfront chemotherapy. If immunostaining is modest and not uniform, this suggests a WT p53 expression pattern. Our data suggest no clear benefit by adding bevacizumab to chemotherapy upfront. If p53 immunostaining is indeterminant, which may occur due to high cellular heterogeneity of p53 expression, cytoplasmic instead of nuclear staining or other conditions, we recommend sequencing TP53. If results reveal a mutation (aother than the known SNP at P72), consideration should be given for adding bevacizumab to chemotherapy upfront. Note that tumors that coexpress POLE and TP53 mutations or potentially those with microsatellite instability or mismatch repair deficiency comprise a special category, and at this time, the data do not inform management. IHC, immunohistochemistry; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; WT, wild-type.