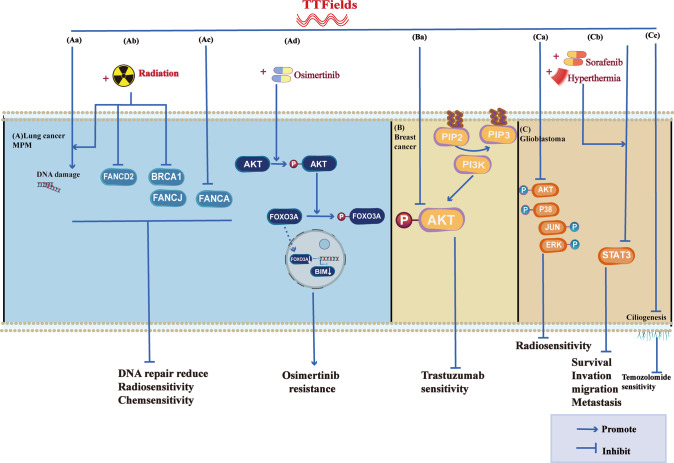
Fig. 2. Molecular pathway changes caused by TTFields combined with radiotherapy or drugs in GBM, MPM, NSCLC, and breast cancer.
A Lung cancer or MPM. A Aa–c TTFields combined with radiation causes DNA damage but reduces DNA damage repair by inhibiting the expression of FANCA, FANCD2, FANCJ, and BRCA. A Ad In addition, TTFields promotes the phosphorylation of AKT, which in turn promotes the phosphorylation of FOXO3A, reduces the nuclear entry of FOXO3A, and inhibits the expression of BIM, which ultimately leads to the weakening of the efficacy of Osimertinib. B Breast cancer. B Ba TTFields enhances breast cancer sensitivity to Trastuzumab by inhibiting AKT phosphorylation. C Glioblastoma. C Ca TTFields inhibits the phosphorylation of AKT, JUN, P38, and ERK, resulting in enhanced radiosensitivity while inhibiting ciliogenesis and enhancing the sensitivity of GBM to Temozolomide. C Cb In addition, TTFields combined with Sorafenib or hyperthermia resulted in cell death by inhibiting STAT3. C Cc TTFields inhibits ciliogenesis, thereby suppressing sensitivity to Temozolomide.