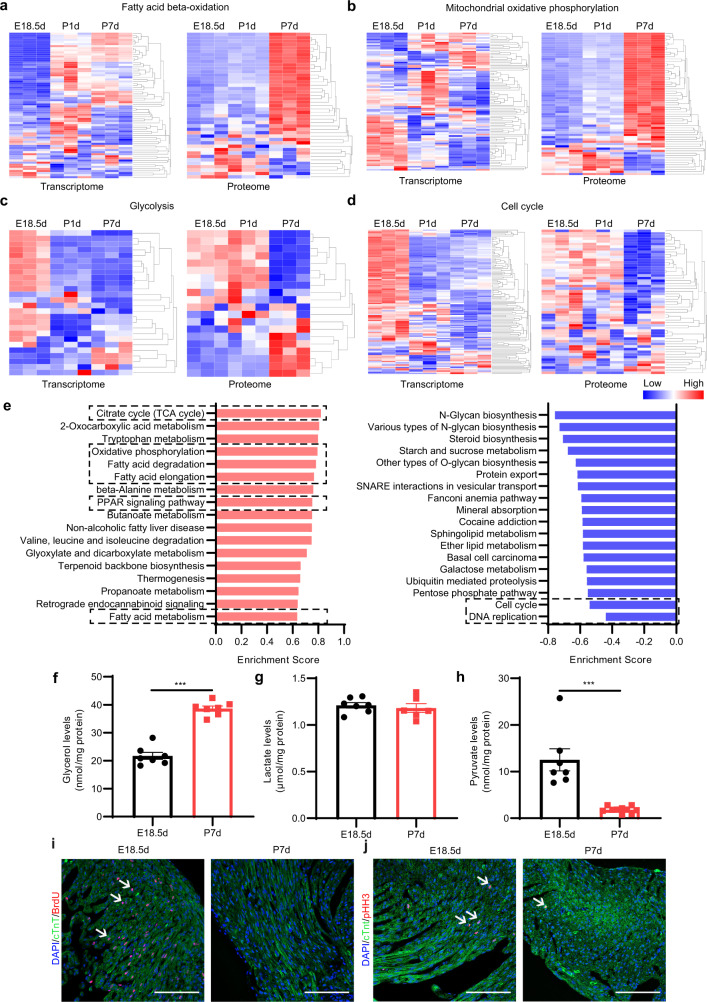
Fig. 1. Metabolic reprogramming and cardiomyocyte cell cycle arrest occur in the neonatal mouse heart.
a–d Heatmap of the mRNA and proteins related to FA beta-oxidation (a), mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (b), glycolysis (c), and cell cycle (d). e Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) of the proteome in perinatal mouse hearts (P7d vs E18.5d). Left: Positive enrichment score (ES). Right: Negative ES. f Glycerol levels in the hearts of E18.5d and P7d mice (n = 7 for each group). g Lactate levels in the hearts of E18.5d and P7d mice (E18.5d, n = 7; P7d, n = 6). h Pyruvate levels in the hearts of E18.5d and P7d mice (E18.5d, n = 7; P7d, n = 10). i Immunofluorescence staining of cTnT and BrdU in the hearts of E18.5d and P7d mice. Scale bar, 50 μm. The white arrows indicate cTnT and BrdU double-positive cells. j Immunofluorescence staining of cTnT and pHH3 in the hearts of E18.5d and P7d mice. Scale bar, 50 μm. The white arrows indicate cTnT and pHH3 double-positive cells. Data are presented as means ± SEM and the P values were determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. ***P < 0.001.