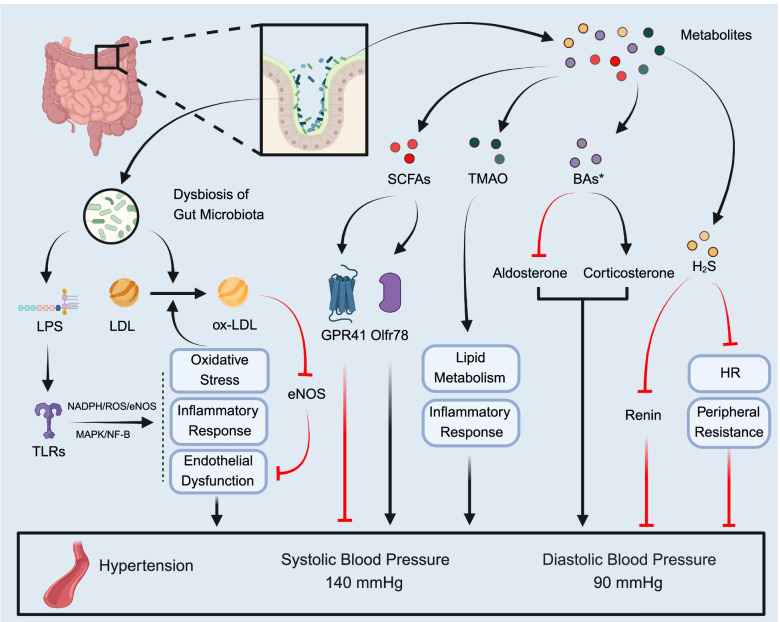
Fig. 4.
The mechanism of gut microbiota increasing the risk of hypertension (created with BioRender.com). Hypertension is diagnosed in adults with systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mmHg. The dysbiosis and metabolites of gut microbiota can influence the course of hypertension. Abbreviations: SCFAs: short-chain fatty acids; TMAO: trimethylamine N-oxide; BAs: bile acids; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; TLRs: Toll like receptors; GPR41: G protein-coupled receptor 41; Olfr78: olfactory receptors 78; HR: heart rate; LDL: low density lipoprotein; ox-LDL: oxidized low-density lipoprotein; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase. *The regulatory effect of BAs on blood pressure is still controversial, and the figure shows only one possible mechanism