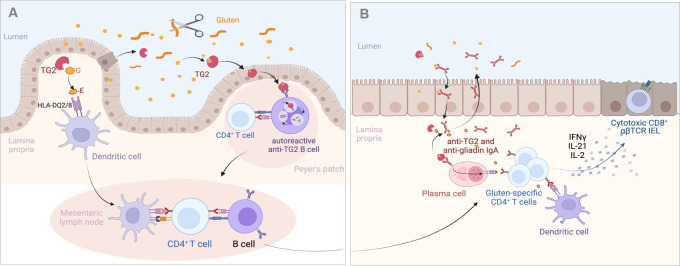
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanisms of the antigluten and antitransglutaminase 2 (TG2) responses in the coeliac intestine. (A) Initiation of the adaptive immune response against gluten and TG2. Gluten peptides left undigested are deamidated by TG2 either in the intestinal lumen where TG2 can be released by extruded dead enterocytes or after crossing the epithelium by TG2 liberated in the extracellular matrix. Deamidated peptides bind HLA-DQ2/8 molecules at the surface of dendritic cells in Peyer’s patches (not shown) or in lamina propria. Dendritic cells can then initiate the activation of gluten-specific T cells in the Peyer’s patches (not shown) or after migration in the mesenteric lymph nodes. Gluten-specific CD4+ T cells cooperate with naïve antigluten B cells to induce the antigluten humoral response. Alternatively, TG2-gluten complexes may cross the Peyer’s patch epithelium and bind to the B cell receptor of autoreactive anti-TG2 B cells present in the lymphoid follicle. TG2-gluten complexes bound to the B cell receptor are endocytosed, processed in B cell endolysosomal compartments, where released gluten peptides can be loaded on HLA-DQ molecules. HLA-DQ-gluten complexes are then translocated at the surface of autoreactive B cells, allowing the activation of gluten-specific CD4+ T cells and simultaneously cooperative interactions that license the IgA response against TG2. (B) Activation of the effector antigliadin CD4+ T cell response. Following their activation in gut lymphoid tissues and mesenteric lymph nodes, gluten-specific effector CD4+ T cells, antigluten and anti-TG2 IgA plasma blasts migrate into the lamina propria. On re-encounter with HLA-DQ-gluten complexes displayed by dendritic cells and by anti-TG2 plasma cells, effector CD4+ T cells secrete cytokines and notably interferon gamma (IFNγ), interleukin (IL)-21 and IL-2, which participate in the activation of CD8+ cytotoxic T intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL). Plasma cells produce IgA antibodies against gluten and TG2 antibodies that are transported into the intestinal lumen. IgA-gluten and IgA-TG2-gluten complexes may be retrotransported across the epithelium and further foster the antigluten response. Created with Biorender.com.