Fig. 3.
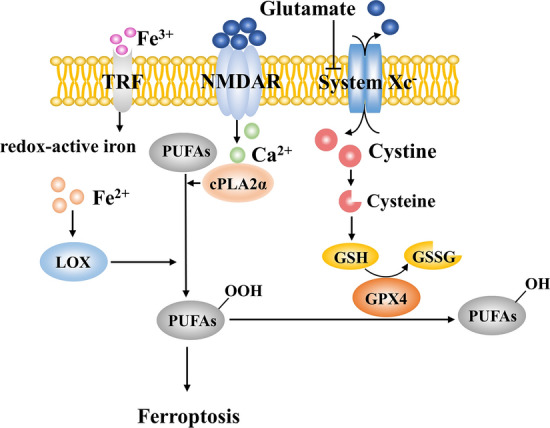
Ferroptosis during cerebral ischemia. Normally, GPX4 uses GSH to catalyze lipid hydroperoxides into alcohols. Increased extracellular glutamate inhibits the activity of System Xc− as well as the cysteine-GSH-GPX4 axis. Meanwhile, Ca2+ overload activates cPLA2α to provide substrates for lipid peroxidation. Fe2+-activated lipoxygenase (LOX) also participates in this process. Increased redox-active iron and overwhelming lipid peroxidation contribute to ferroptosis. cPLA2α, cytosolic phospholipase A2α; GPX4, γ‐L‐glutamyl‐L‐cysteinylglycine peroxidase 4; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; LOX, lipoxygenase; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; TRF, transferrin.
