Fig. 1 |. RNA cellular functions.
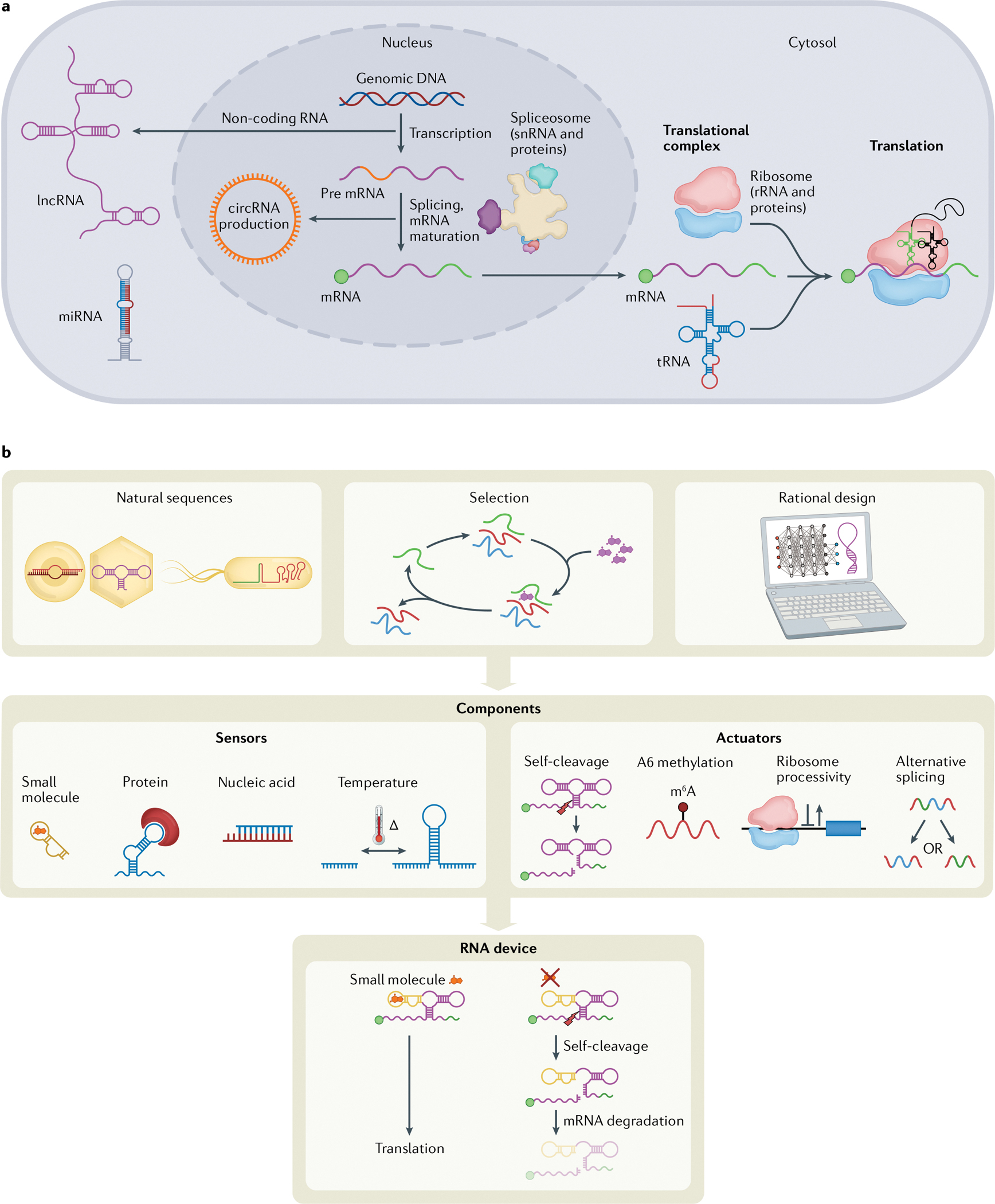
a | Following transcription, mRNAs are spliced by the spliceosome, a complex of small nuclear RNAs (snRNA) and proteins, and matured by the addition of markers such as a 5′ cap (green circle) and polyA tail (green line)147,148. Outside the nucleus, the canonical function of RNA is the combination of tRNAs, ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) (with accompanying ribosomal proteins, making up the ribosome) and mRNAs to form translational complexes that produce most cellular proteins. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are RNA molecules that form naturally via lariat intermediates as a splicing by-product149. RNA regulation of cellular processes can be accomplished by circRNAs, as well as long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) that can regulate levels of exogenous RNA, endogenous RNA and protein expression150,151. b | RNA device engineering. Parts for RNA devices can be obtained by mining natural sequences, selection experiments or rational design of sequences. Sensing and actuating components can be characterized and combined to form an RNA device with both sensing and actuation capabilities.
