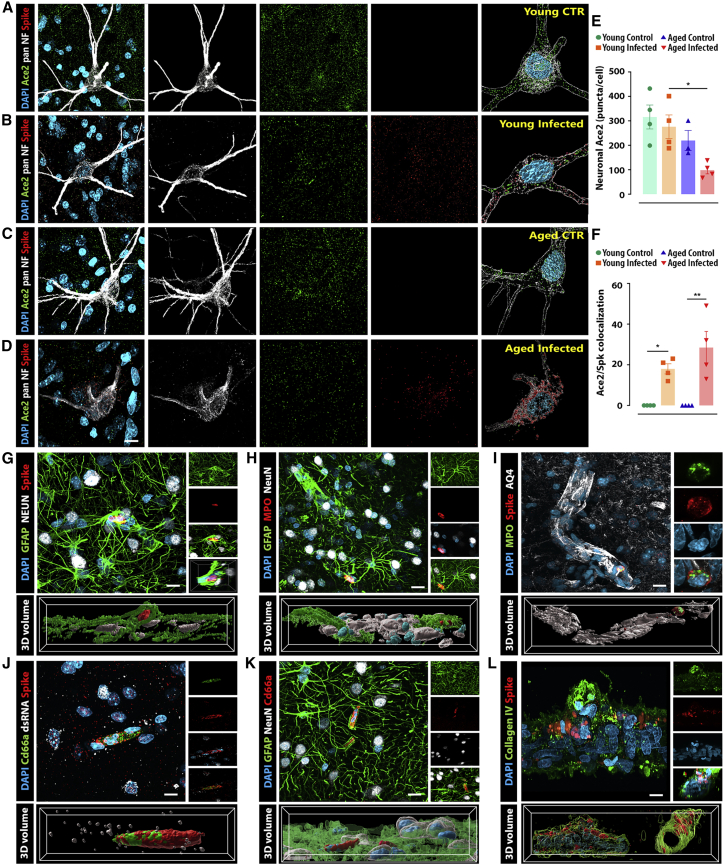
Figure 3.
SARS-CoV-2 infection induces blood vessel disruption, reactive neutrophil recruitment, and ACE2 receptor downregulation
(A–D) Airyscan super-resolution microscopy was applied to quantify ACE2 and Spk protein expression and binding within olfactory neurons (pan-NF maker) across the different experimental groups.
(E) ACE2 expression is substantially reduced in the neurons of aged, infected animals compared with young, infected controls.
(F) In addition, around 15%–40% of the remaining receptors colocalize with Spk protein in both infected groups. Multiple structural abnormalities in the BBB were observed across the olfactory cortex of infected monkeys.
(G) Neurons (NeuN) and astrocytes (GFAP) present high levels of ACE2 expression and are also the major cell types expressing Spk protein.
(H) Notably, disrupted blood vessels are associated with activated neutrophils (MPO) and robust recruitment of reactive astrocytes.
(I) Altered BBB was also confirmed using aquaporin 4 (AQ4), a water channel expressed in astrocytic endfeet and involved in edema formation.
(J and K) Additionally, the identity of neutrophils was confirmed using the CD66a marker, recruited to the injury.
(L) Isolated blood vessels from surrounding meninges also show viral expression.
Scale bars, 10 μm (A–D), 50 μm (G–K), and 5 μm (L). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc test. Numerical data are represented as mean ± SEM.