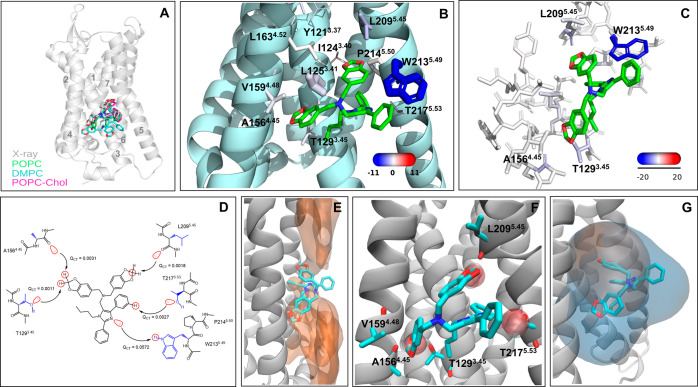
Figure 2.
Extrahelical allosteric site of C5aR1 and its interactions from MD simulations and quantum chemical calculations. (A) Overall location of NDT9513727 in C5aR1. The overlay of the X-ray position with the average position of NDT9513727 in the POPC, DMPC, and POPC-Chol simulations. The helices are labeled. (B) Zoomed view of the binding site. The key residues forming contacts with NDT9513727 are shown in stick representation. The size and color of the residues correspond to the relative strength of van der Waals and electrostatic interactions with the ligand, respectively. The actual values of the interaction energies are shown in Table S9. (C) Electrostatic energy from the F/I-SAPT calculations mapped to the allosteric site residues. (D) 2D view of the key NDT9513727–C5aR1 interactions and the value of the QCT descriptor. The orbital interactions responsible for charge transfer (QCT) between a donor and an acceptor are visualized in red. The direction of the charge transfer is shown by arrows. The backbone and the side chain of residues are colored black and blue. (E) Low-energy lipid area (in orange surface) in the allosteric site obtained from the grid free energy calculation based on the POPC simulations of the receptor empty form. (F) Overlay of NDT9513727 (in stick) and a water molecule (in transparent SPK representation) from the MD simulations. In the simulations of the receptor empty form, water molecules frequently occupy the binding pocket of the dioxolane ring, forming H-bonding interactions with the backbone of A156, V159, and L209 and the side chain of T129 and T217. (G) Overlay of the allosteric cavities from MDpocket calculation with the selection of only receptor atoms (orange surface) and receptor–lipid atoms (blue surface). The ligand is shown for clarity of the allosteric site location. The results are shown for the POPC simulations, and the others can be found in Figure S2. The lipid atoms were selected at a distance of 6 Å from the selected receptor atoms.