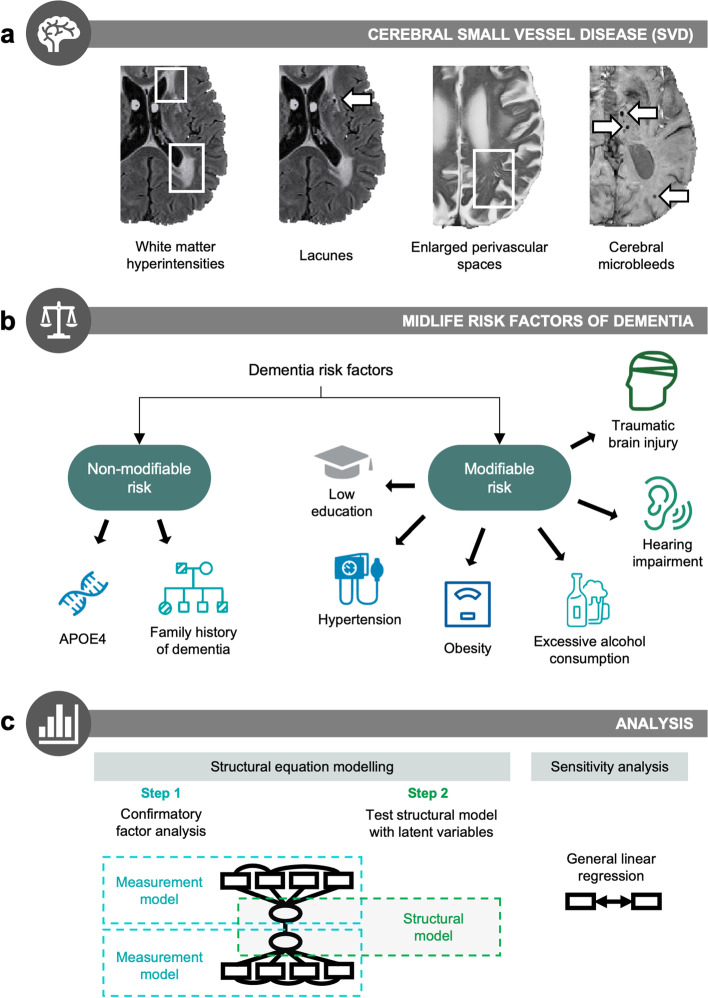
Fig. 2.
Overview of methodology. a Cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) was quantified on 3T MRI using four imaging markers: white matter hyperintensities, lacunes, enlarged perivascular spaces, and cerebral microbleeds. b Midlife risk factors were classified into two categories: non-modifiable (inherited) risk vs. modifiable risk factors. Non-modifiable risk factors were APOE4 and parental family history of dementia. Modifiable risk factors were based on the risk factors identified in the 2020 Lancet Commission report for dementia prevention [12] (early to mid-life risk factors). c Structural equation modelling was performed to assess associations between the latent variables of modifiable risk and SVD. The first stage tests the measurement model using confirmatory factor analysis. If measurement models achieve good fit, the second stage tests the full structural model. As a form of sensitivity analysis, results were replicated using general linear regression models to determine the robustness of results across different methods. Detailed statistical procedures can be found under the “Methods” section