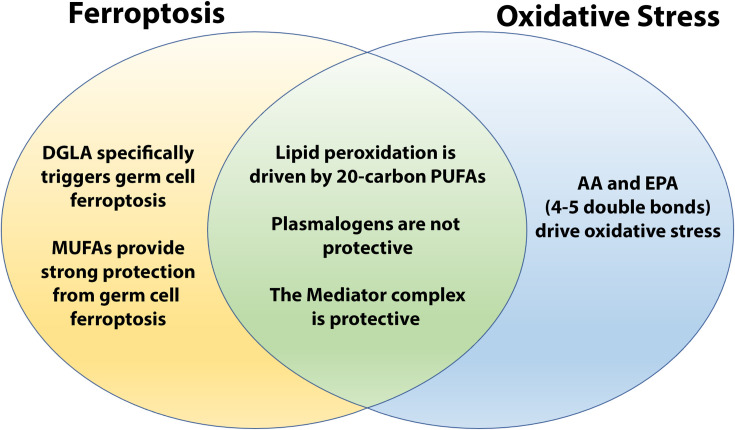
Fig 6. Similarities and differences between DGLA-induced ferroptosis and TBHP-induced oxidative stress.
Ether lipid deficiency in C. elegans results in increased sensitivity to 20-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) through germ cell ferroptosis specifically induced by dietary and endogenous dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA; 20:3(n-6)) and to oxidative stress that requires the highly unsaturated PUFAs, arachidonic acid (AA; 20:4(n-6)) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; 20:5(n-3)). In both cases, the Mediator complex is protective while plasmalogens do not play an active role in protection as an endogenous antioxidant. Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) strongly protect worms from DGLA-induced ferroptosis.