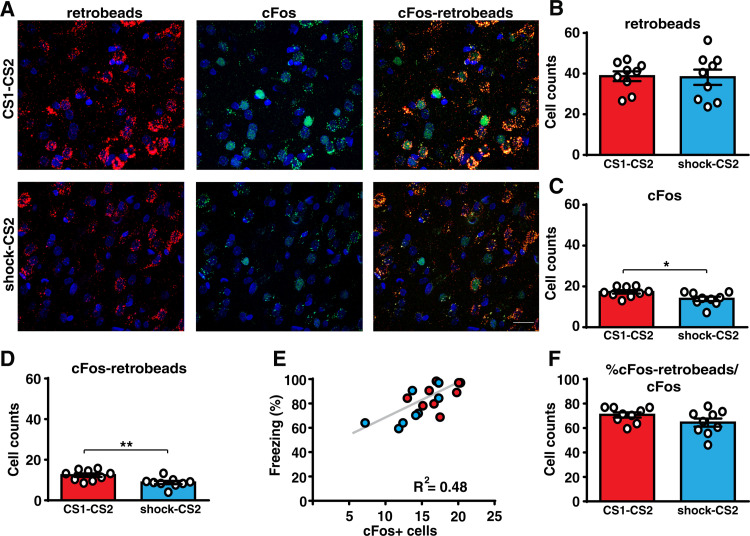
Fig 2. Prior auditory fear learning increases the activity in the Te2-to-BLA pathway.
(A and B) The number of neurons within layer 2/3 of the Te2 projecting to the BLA (retrobeads-labeled) was similar between animals that were trained in two different CS-US associations (CS1-CS2, n = 9, upper panel) and in those who received only painful stimuli followed by the CS2-US association 2 weeks later (shock-CS2, n = 9, lower panel) (Student t test, t(16) = 0.11, p = 0.9132, Glass’s delta = 0.006). Scale bars, 20 μm. (C) After retention of the recent fear memory, the expression of cFos protein was higher in the CS1-CS2 group (Student t test, t(16) = 2.49, p = 0.0238, Cohen’s d = 0.117). (D) Importantly, the number of cells that project from the Te2 to the BLA and that colocalized with cFos expression was higher in this group (Student t test, t(16) = 3.05, p = 0.0076, Cohen’s d = 2.99). (E) Freezing of CS1-CS2 and shock-CS2 rats to the recent CS correlated with the number of cFos positive cells in Te2 (Pearson’s correlation, r = 0.69, p = 0.0013). (F) The percentage of double-positive cells on the total cFos positive cells was similar between the 2 groups (Student t test, t(16) = 1.59, p = 0.1302, Glass’s delta = 0.627). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. All data are mean and SEM. The summary data for Fig 2 can be found in Supporting information in the file named S2 Data. BLA, basolateral amygdala; CS, conditioned stimuli; US, unconditioned stimulus.