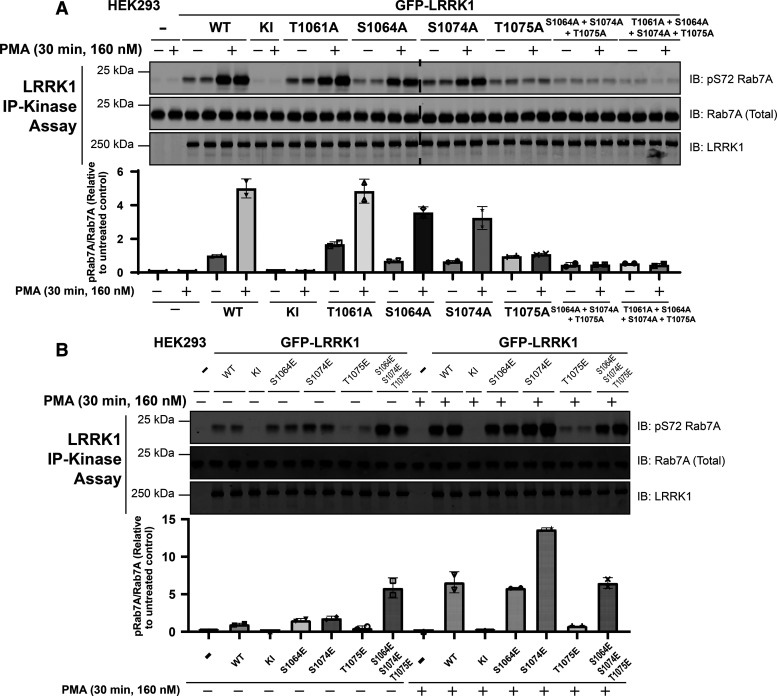
Figure 7. Mutations to Ser1064, Ser1074 and Thr1075 impact phorbol ester dependent LRRK1 activation.
(A and B) HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding wild type (WT), kinase-inactive (KI) LRRK1[D1409A] or the indicated mutants of GFP-LRRK1. Ala mutants to block phosphorylation were studied in (A) and Glu mutants to mimic phosphorylation were investigated in (B). Twenty-four hours post transfection, cells were serum-starved for 16 h and stimulated ± 160 nM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) for 30 min. Cells were lysed and GFP-LRRK1 immunoprecipitated using an anti-GFP nanobody from 1 mg of cell extract. LRRK1 kinase activity towards recombinant Rab7A was assessed in a 30 min assay. Reactions were terminated by addition of SDS-sample buffer and levels of pSer72-Rab7A, Rab7A and LRRK1 were assessed by quantitative immunoblot analysis using the LI-COR Odyssey CLx Western Blot imaging system with the indicated antibodies. Combined immunoblotting data from two independent biological replicates (each performed in duplicate) are shown. Lower panel quantified immunoblotting data are presented as ratios of pRab7ASer72/total Rab7A (mean ± SEM) relative to levels observed with the activity of non-stimulated wild-type LRRK1.