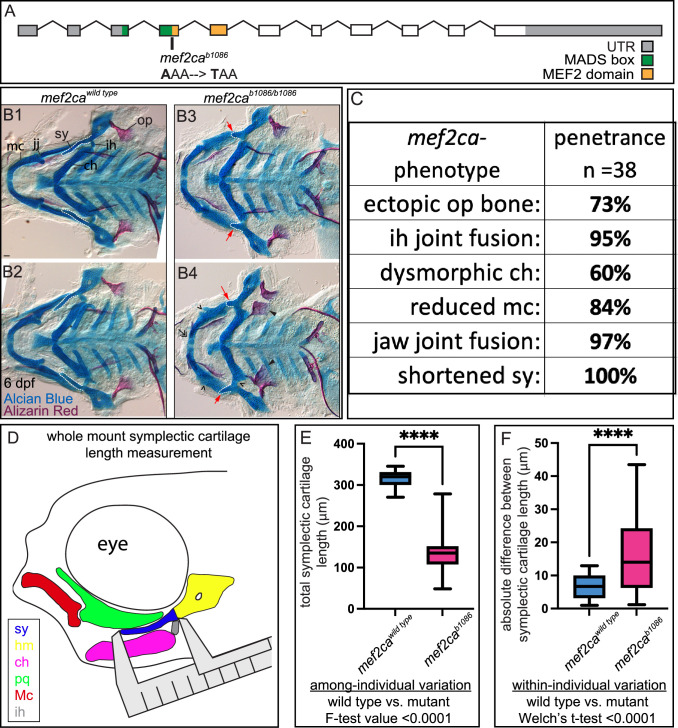
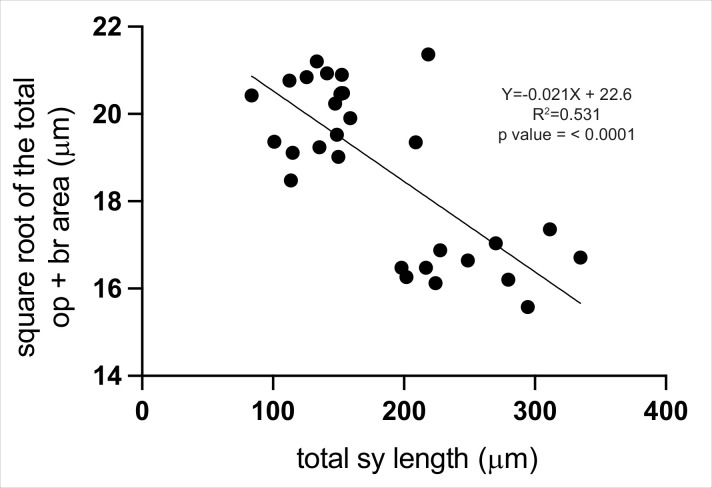
Figure 1. mef2ca mutant craniofacial phenotypes are more variable than wild types.
(A) Schematic of mef2ca exonic structure. The mef2cab1086 mutant allele used in this study and regions encoding known functional domains are annotated. (B1–B4) Zebrafish heterozygous for mef2ca were pairwise intercrossed, and 6 days post fertilization (dpf), larvae were stained with Alcian blue and Alizarin red to label cartilage and bone. The individuals were then genotyped, flat mounted, and imaged. Two examples (upper and lower) are provided for each genotype. The following craniofacial skeletal elements are indicated in a wild-type individual: opercle bone (op), branchiostegal ray (br), Meckel’s (mc), ceratohyal (ch), symplectic (sy) cartilages, interhyal (ih), and jaw (jj) joints. Indicated phenotypes associated with mef2ca mutants include: ectopic bone (arrowheads), interhyal and jaw-joint fusions (^), reduced mc (double arrowhead), and a shortened sy (red arrows). Dashed outline indicates symplectic cartilage. Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) The penetrance of mef2ca mutant-associated phenotypes observed in 6 dpf homozygous mutant larvae is indicated. (D) Schematic indicating how the symplectic cartilage length was measured in this study. (E) Symplectic cartilage length was measured from 6 dpf wild type or homozygous mutant larvae. The p-value from a Welch’s t-test is indicated (****≤0.0001). F-test value testing for significant differences in variation between genotypes is indicated. (F) Symplectic cartilage length on left and right sides of 6 dpf zebrafish was measured to determine fluctuating asymmetry, or the absolute difference between left and right, for wild type or mutant larvae. The p-value from a Welch’s t-test is indicated (****≤0.0001). For box and whisker plots, the box extends from the 25th to 75th percentiles. The line in the middle of the box is plotted at the median, and the bars are minimum and maximum values. For E and F, n=22 for wild types and 44 for mutants.