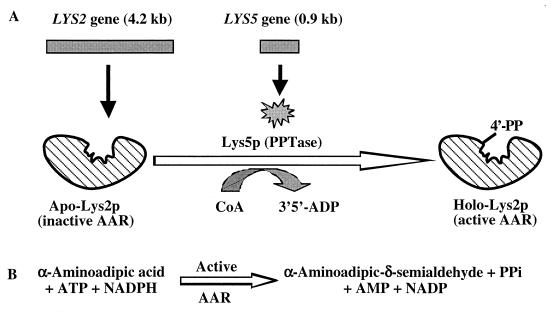
FIG. 1.
Involvement of two distinct genes (LYS2 and LYS5) and enzymes in the complex AAR reaction for the biosynthesis of lysine in C. albicans. (A) The LYS2 gene produces an apo-Lys2p (inactive AAR). The LYS5 gene produces Lys5p, which serves as a PPTase and catalyzes the transfer of 4′-phosphopantetheine (4′-PP) from CoA to the serine 884 of the activation domain of Lys2p. The resulting holo-Lys2p serves as the active AAR. (B) Posttranslationally activated AAR catalyzes the conversion of α-aminoadipic acid to α-aminoadipic-δ-semialdehyde in the presence of ATP and NADPH.