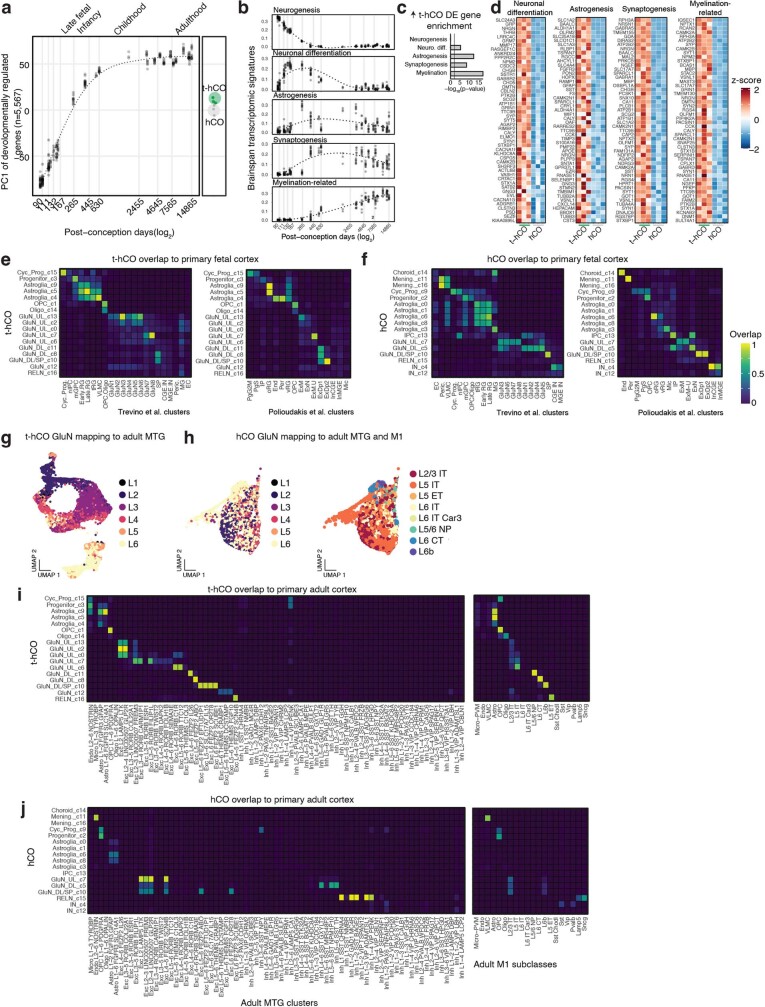
Extended Data Fig. 5. Transplanted hCO RNA-seq comparisons to fetal and adult human cortex.
a. Left: The first principal component (PC1) calculated on gene expression (log base 2 RPKM, reads per kilobase of exon per million reads mapped) from human cortical BrainSpan samples23 and pseudobulk (Methods) snRNA-seq samples using previously defined developmentally regulated genes38. Right: PC1 values for t-hCO and hCO samples. b. The sample weights (Methods) of five neurodevelopmental transcriptomic signatures identified by Zhu et al.38 across human cortical BrainSpan samples. Dashed lines denote fitted curves by LOESS regression. c. Gene set enrichment analysis (one-sided Fisher’s exact test) using the top 200 genes from each neurodevelopmental signature with significantly up-regulated (adjusted P-value < 0.05) t-hCO genes from pseudobulk GluN clusters (neurogenesis, neuronal differentiation, and synaptogenesis signatures), Astroglia clusters (astrogenesis signature), and from pseudobulk of all clusters (myelination-related signature). Line denotes Bonferroni corrected P-value of 0.05. d. Gene expression (pseudobulk and scaled) of the top 50 significantly upregulated t-hCO genes (ranked by differential expression p-value significance) for each signature. e–f. Heat maps of t-hCO (e) and hCO (f) cluster overlap by RNA-seq integration with primary human fetal cortical cell clusters19,20. Cell cluster labels are from original studies. RG, radial glia; Cyc.prog, cycling progenitors; tRG, truncated radial glia, mGPC, multipotent glial progenitor cell; OPC/Oligo, oligodendrocyte progenitor cell/oligodendrocyte; nIPC, neuronal intermediate progenitor cell; GluN, glutamatergic neuron; CGE IN, caudal ganglionic eminence interneuron; MGE IN, medial ganglionic eminence interneuron; EC, endothelial cell; MG, microglia; Peric., Pericytes; PgG2M and PgS, cycling progenitors; IP, intermediate progenitor; oRG, outer radial glia; End, endothelial cell; Per, pericyte; vRG, ventricular radial glia; ExM, maturing excitatory neuron; ExN, excitatory neuron; ExM.U, maturing upper layer excitatory neuron; ExDp, excitatory deep layer neuron; In, interneuron. g–h. UMAP visualization of GluN cell type classification of t-hCO (g) and hCO (h) using label transfer (methods) from adult human cortical single nuclei RNA-seq reference datasets. Transfer labels from dissected cortical layers of medial temporal gyrus (MTG)21 shown in g and to the left in h. Right (h): transfer labels from annotated GluN subclasses from motor cortex (M1)22. I–j. Heat maps of t-hCO (i) and hCO (j) cluster overlap by RNA-seq integration with primary human adult cortical cell clusters21,22. Cell cluster labels are from original studies. Exc, excitatory neuron; Inh, inhibitory neuron; Astro, astrocyte; Endo, endothelial cells; CT, corticothalamic cell; ET, extratelencephalic cell; IT, intratelencephalic cell; micro, microglia; NP, near-projecting; oligo, oligodendrocyte; OPC, oligodendrocyte precursor; PVM, perivascular macrophage; VLMC, vascular and leptomeningeal cells.