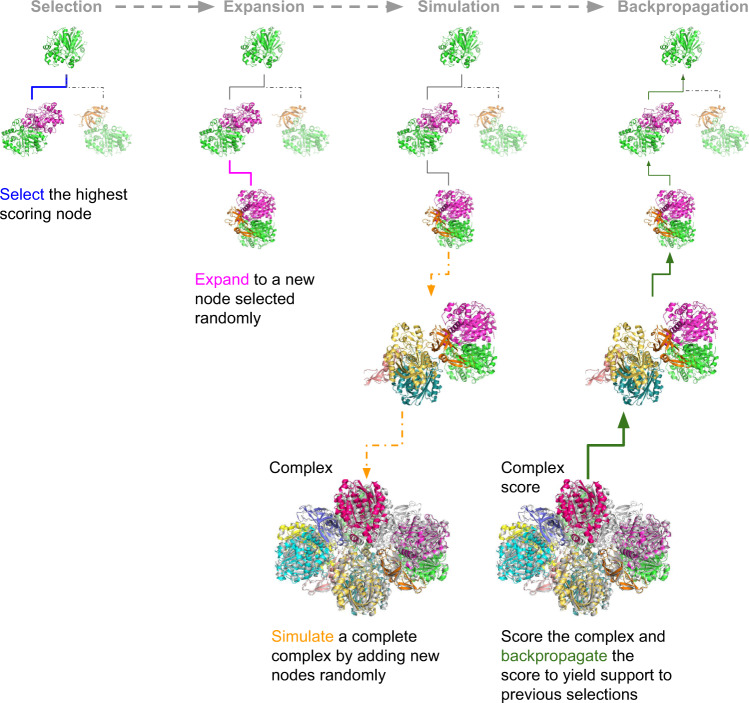
Fig. 2. Monte Carlo tree search.
Starting from a node (subcomplex) a new node is selected based on the previously backpropagated scores. From this node, a random node is added (expansion). A complete assembly process is then simulated by adding nodes randomly until an entire complex is assembled or a stop caused by too much overlap is reached. The complex is scored, and the score is backpropagated to all previous nodes, which yields support for the previous selections. The final result is that the nodes most likely to result in high-scoring complexes are joined in a path containing all chains. The principle for the complex 6ESQ is shown.