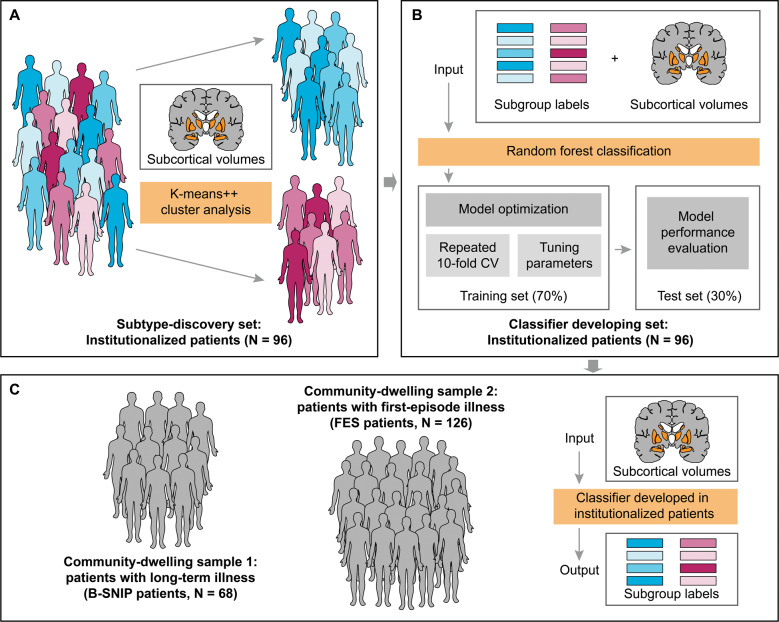
Fig. 1. Schema of subtype discovery, classifier development, and patient assignment.
Subtypes were identified using K-means ++ cluster analysis with regional subcortical volumes in institutionalized patients with schizophrenia (A). These institutionalized patients were subsequently used to develop a brain-based classifier with a random forest algorithm, and subgroup labels generated in cluster analysis and regional subcortical volumes applied in cluster analysis were as input of the classifier (B). The classifier developed in institutionalized patients was applied to classify community-dwelling schizophrenia individuals with long-term illness or first-episode illness (C). B-SNIP, the Bipolar-Schizophrenia Network on Intermediate Phenotypes consortium; CV, cross-validation; FES, first-episode schizophrenia; N, number of patients.