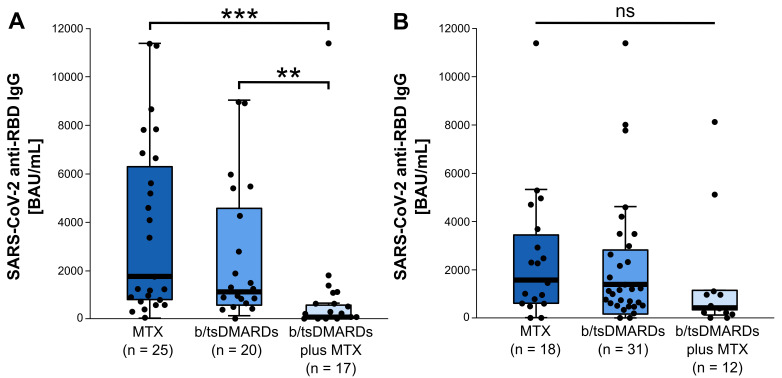
Figure 1.
SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike protein receptor binding domain (RBD) IgG serum levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. (A) Elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (≥ 64.5 years, n=62) receiving b/ts DMARDs with concomitant MTX therapy show significantly lower SARS-CoV-2 anti RBD IgG serum levels (64.8 (20.8, 600.3) BAU/mL, n=17) compared with patients receiving MTX monotherapy (1743.8 (734.5, 6779.6) BAU/mL, n=25) or b/tsDMARSs monotherapy (1106.0 (526.3, 4965.2) BAU/mL, n=20) (median (IQR)) (p<0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test). (B) in the younger RA patient subgroup (< 64.5 years, n=61), no differences of SARS-CoV-2 anti-RBD IgG serum levels were found between MTX monotherapy (1566.9 (584.3, 3724.7) BAU/mL, n=18), b/tsDMARDs monotherapy (1385.9 (137.9, 2971.8) BAU/mL, n=31) and b/tsDMARDs with concomitant MTX (417.8 (326.1, 1141.8) BAU/mL, n=12) (median (IQR)) (p=0.334, Kruskal-Wallis test). Data are presented as box blots with horizontal bars representing the median. Pairwise comparison using the Dunn-Bonferroni approach, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. As we also included patients with other treatment modalities, for example, leflunomide monotherapy and no therapy, which are not part of this figure, the number of patients is reduced (n=62, n=61, respectively) compared with the whole study cohort. BAU, binding antibody; bDMARDs, biological DMARDs; MTX, methotrexate; NS, not significant; tsDMARDS, targeted synthetic DMARDs (disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs).