Figure 2.
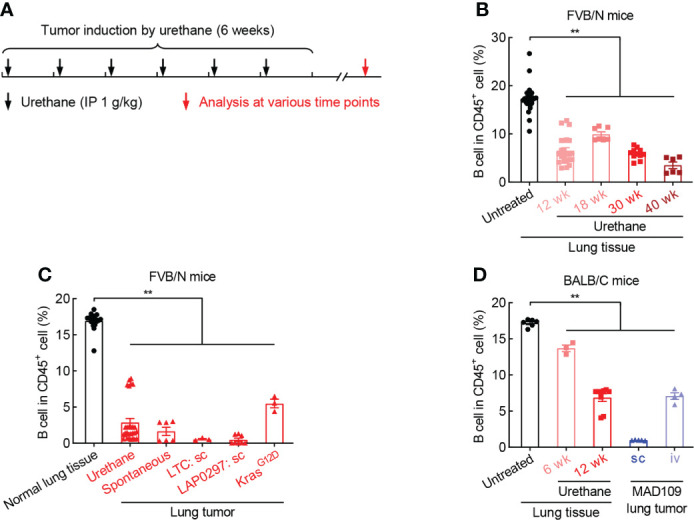
B cell is reduced during lung tumorigenesis. (A) Schematic of smoking carcinogen urethane-induced endogenous lung tumorigenesis. (B) FACS data showing decrease of B cell in lung tissues exposed to urethane in FVB/N mice. Untreated (n = 24), Urethane 12 wk (n = 23), Urethane 18 wk (n = 7), Urethane 30 wk (n = 11), Urethane 40 wk (n = 6). (C) FACS data showing decrease of B cell in multiple lung tumor models in FVB/N mice. Normal lung tissue (n = 17), Urethane-induced lung tumor (n = 28), Spontaneous lung tumor (n = 6), LTC sc (n = 3), LAP0297 sc (n = 8), KrasG12D-induced lung tumor (n = 3). (D) FACS data showing loss of B cell in both urethane-induced endogenous lung tumor and xenograft models in BACL/C mice. Untreated (n = 6), Urethane 6 wk (n = 3), Urethane 12 wk (n = 9), MAD109 sc (n = 5), MAD109 iv (n = 4). LTC: Lung Tumor Cell which was established from spontaneous FVB/N lung tumor in our laboratory. LAP0297 and MAD109 are lung cancer cell lines originally derived from spontaneous lung tumors developed in FVB/N and BALB/C mice, respectively. sc, subcutaneous injection; iv, intravenous injection (tail vein). Ordinary one-way ANOVA was performed. Data represented means ± SEM (B-D). **p < 0.01.
