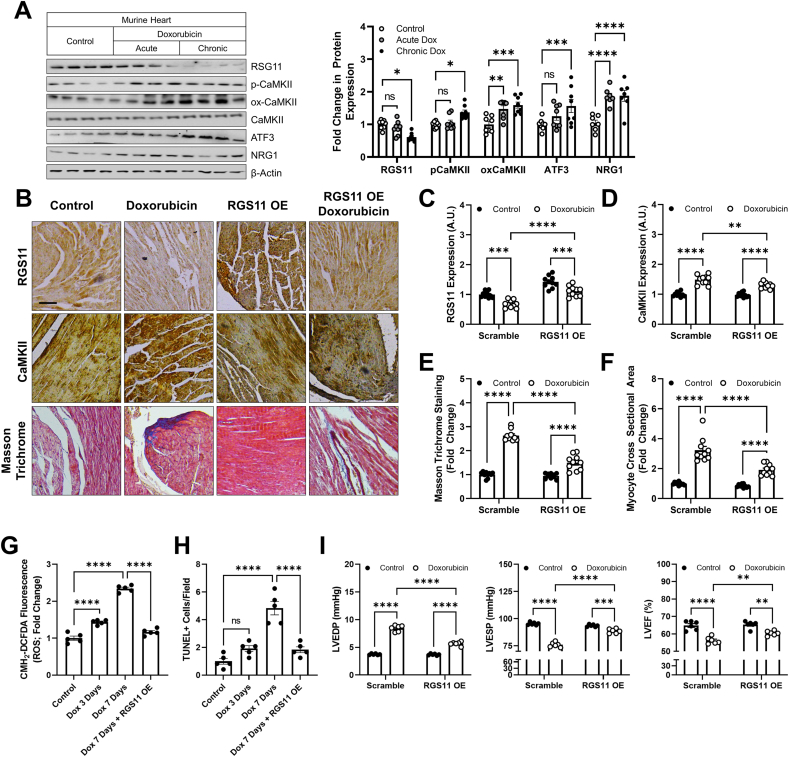
Fig. 7.
Cardiac-specific RGS11 OE protects against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in mice. (A) Mice were treated with doxorubicin (cumulative dose of 45 mg/kg i. p.) or saline control over 8 weeks (chronic) or mice were given a single dose of doxorubicin (20 mg/kg i. p.) or saline and sacrificed after 3 days (acute). Cardiac tissues were collected from both the sets for protein expression analyses of RGS11, p-CaMKII, ox-CaMKII, CaMKII and ATF3 (n = 8). (B–G) An RGS11 encoding viral construct or control (Ad-β-gal) was introduced into the myocardium. After 15 days, animals were given saline or doxorubicin (cumulative dose of 45 mg/kg i. p.) over 8 weeks. After 8 weeks cardiac phenotyping was performed, and tissues samples collected 1 week later for biochemical and histological analyses. (B) Representative images [scale bar = 100 μm] of RGS11 and CaMKII immunohistochemistry and cardiac fibrosis (Masson Trichrome staining). Quantification of (C) RGS11 and (D) CaMKII histoscores (n = 10). (E) Quantification of collagen deposition (fibrosis, n = 10). (F) Average myocyte cross sectional area (n = 10). (G) CM-H2-DCFDA fluorescence (total ROS; n = 5). (H) TUNEL positive cells (n = 5). (I) Cardiac parameters (n = 6). β-Actin serves as a loading control for western blots. Immunoblots are accompanied by a densitometric quantification wherein expression is normalized to the corresponding control group. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Sidak's post-hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. ns = not significant. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.