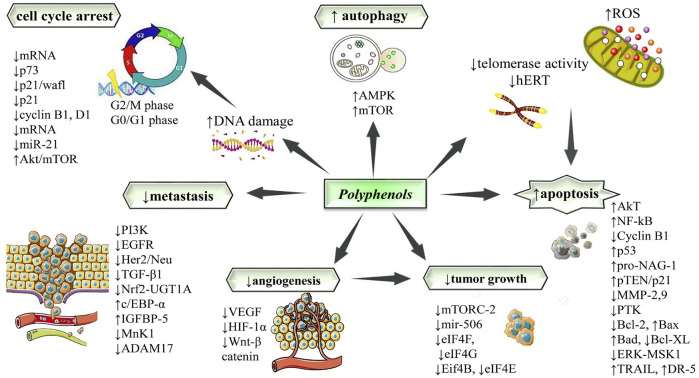
FIGURE 2.
Potential molecular targets and signaling pathways for the antitumor effect of polyphenols. Symbols: ↑increase, ↓decrease. Abbreviations: ADAM17, ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17; Akt/mTOR, protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; BAD, Bcl-2 antagonist of cell death; Bax, Bcl2-Associated X Protein; Bcl-2, B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 protein; Bcl-xL, B-cell lymphoma-extra large; c/ebp-α, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha; DR-5, death receptor 5; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK/MSK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen- and stress-activated kinase 1; Her2/Neu, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2/neutrophills; HIF-1-alpha, hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; IGFBP-5, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5; hTERT, human telomerase reverse transcriptase; miR, microRNA; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MnK-1, a family of serine/threonine kinases; mRNA, messenger ribonucleic acid; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; mTORC2, mTOR Complex 2; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; Nrf1, nuclear respiratory factor 1; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; pro-NAG-1, pro-nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1; pTEN, phosphatase and TENsin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; PTK, protein tyrosine kinase; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor-β1; TRAIL, tumor-necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand; UGT1A, UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; Wnt, wingless-related integration site.