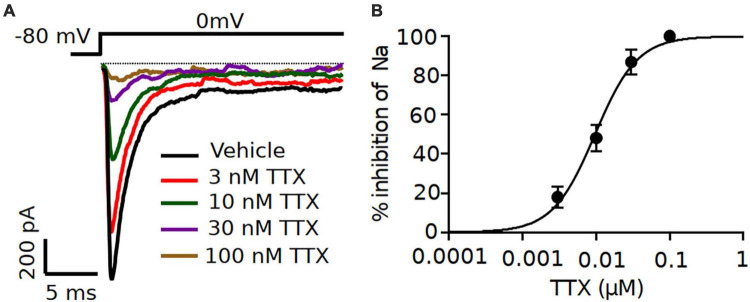
FIGURE 2.
Increasing concentrations of TTX resulted in a concentration-dependent inhibition of Na+ currents in mouse cortical pyramidal neurons. (A) Representative traces of Na+ currents from pyramidal neurons recorded in vehicle condition and in presence of TTX at concentrations of 3, 10 30 and 100 nM. Inhibition by TTX of Na+ currents were elicited by a 20-ms pulse depolarized from a holding potential of –80 mV to 0 mV. (B) Concentration-response relationship for TTX inhibition of Na+ current in pyramidal neurons. Each point shows Na+ peak current relative to vehicle averaged over 7 neurons, except for 100 nM TTX (n = 3). The solid line is the best fit of the average data to the Hill equation yielding IC50 = 9.2 nM.