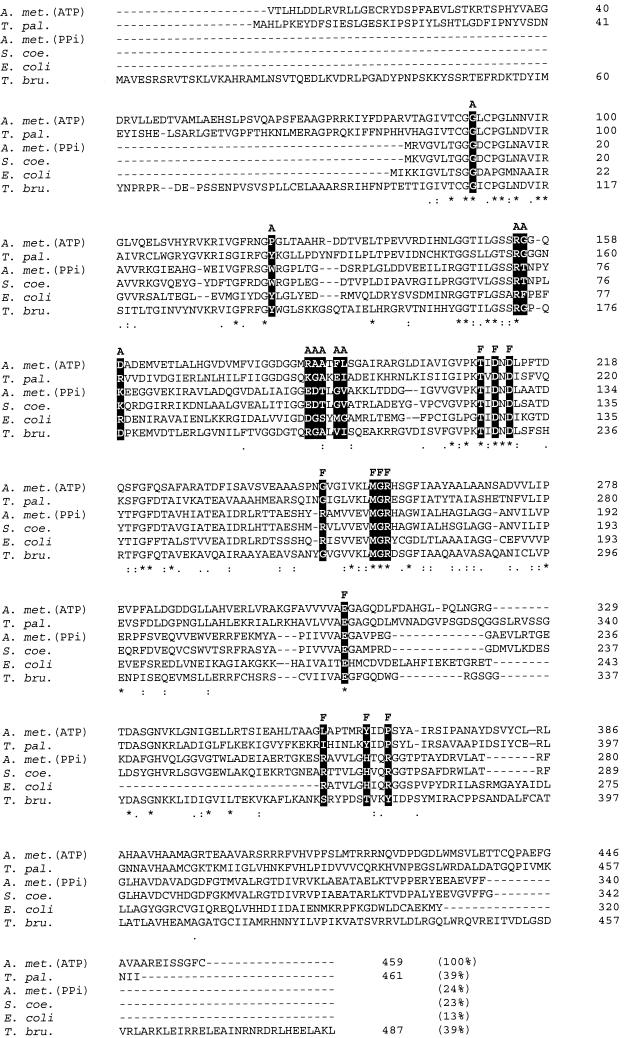
FIG. 4.
Clustal W (36) multiple alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence of the ATP-PFK from A. methanolica with the sequences of the PFKs from S. coelicolor A3(2) (National Center for Biotechnology Information [NCBI] accession number 008333), E. coli (NCBI accession number KIECFA), T. pallidum (NCBI accession number A71366), and T. brucei (NCBI accession number AAC47836) and the PPi-PFK from A. methanolica (NCBI accession number Q59126). The percent similarity between the ATP-PFK from A. methanolica and each of the other PFKs is indicated in parentheses. A and F indicate residues (solid boxes) involved in binding of ATP and F-6-P, respectively, in the E. coli ATP-PFK enzyme (34). *, position with a fully conserved amino acid residue; :, position with a fully conserved strong group (STA, NEQK, NHQK, NDEQ, QHRK, MILV, MILF, HY, and FYW); ., position with a fully conserved weaker group (CSA, ATV, SAG, STNK, STPA, SGND, SNDEQK, NDEQHK, NEQHRK, FVLIM, and HFY).