Figure 3.
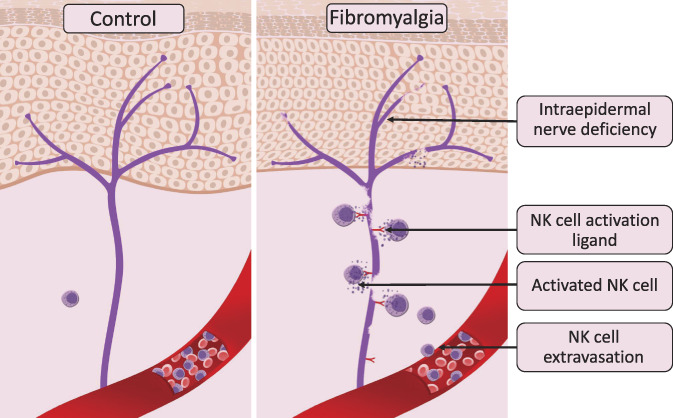
The contribution of natural killer cells to the pathogenesis of fibromyalgia based on the results of unbiased immune profiling of fibromyalgia cases and controls (based on Verma et al).84 Panels show intraepidermal innervation (purple) in control human subjects (left) and patients with fibromyalgia (right). In those with fibromyalgia, but not in the control subjects, intraepidermal nerves express a ligand for NK cell activation, which in turn coaxes NK cells to extravasate from the bloodstream and follow the ligand's gradient. Thus, depletion of NK cells can be observed in blood samples of patients with fibromyalgia compared with control subjects. The NK cells recruited to the damaged nerve are activated through the immune synapse formation, leading to peripheral nerve degeneration through NK cell cytotoxic functions. Thus, the chronic expression of an NK activation ligand(s) stimulates chronic extravasation, recruitment, and activation of circulating NK cells, resulting in persistent peripheral nerve degeneration, and chronic activation of NK cells. NK, natural killer.
