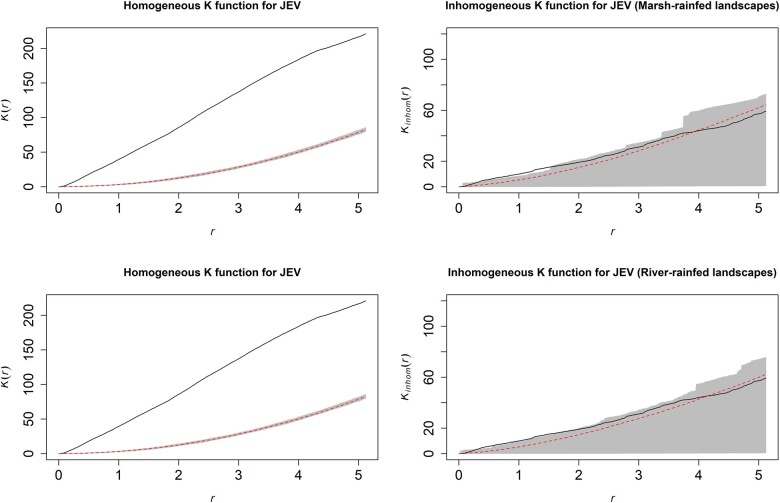
Figure 4.
Homogeneous (left panels) and inhomogeneous (right panels) K-functions for the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) outbreak point process. The homogeneous K-function is not an appropriate fit due to the spatial dependency in JEV outbreaks as depicted by the divergent empirical (solid line) and theoretical functions (the latter is the theoretical function under complete spatial randomness, represented by the dashed line with confidence bands in grey). In contrast, the freshwater marsh-fragmented rain-fed agriculture (top) and river-fragmented rain-fed agriculture (bottom) model-based inhomogeneous K-functions show that the spatial dependency was accounted for by the model covariates (overlapping empirical and theoretical functions). The x-axes, r, represent increasing radii of subregions of the window of JEV outbreaks, whereas the y-axes represent the K-functions.