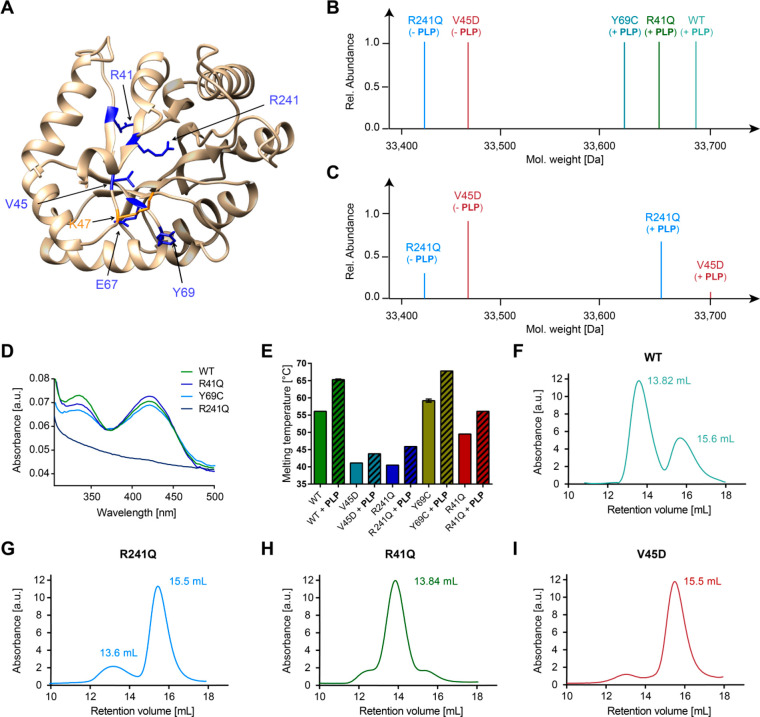
Figure 2.
Impact of pathogenic mutations on PLPBP cofactor binding, stability, and oligomerization. (A) Localization of mutated residues (blue) on the human wild type PLPBP model structure (derived from SWISS-MODEL23 using the yeast ortholog as template, PDB 1B54(13)). The PLP-binding site (K47) is colored orange. (B) Intact-protein MS of WT and mutants after reduction with NaBH4. (C) Intact-protein MS of V45D and R241Q mutants after incubation with a 4-fold molar excess of PLP followed by NaBH4 reduction. (D) UV/vis spectra of PLPBP WT and mutants. (E) Thermal stability of PLPBP WT and mutants in the absence or presence of PLP (20-fold molar excess). (F–I) Analytical size-exclusion chromatograms of WT, R241Q, R41Q, and V45D mutants under reductive conditions, respectively.