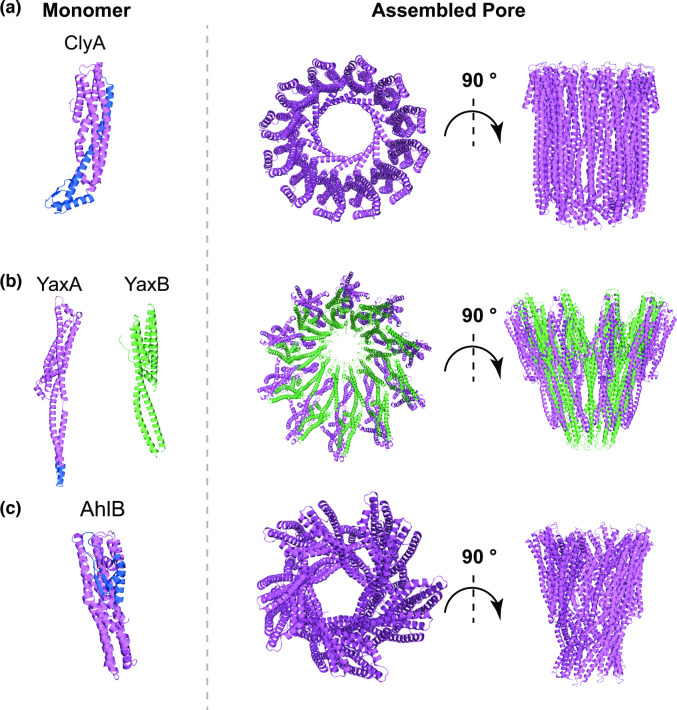
Fig. 2.
Cartoon representation of the molecular structure of the monomer (left), top and side view of the complete pore (right) for monopartite (a), bipartite (b) and tripartite (c) members of the ClyA family. In (a), PDB entry 1QOY was used to obtain the cartoon representation of ClyA monomeric structure and PDB entry 2WCD for its final pore structure. (b) The monomeric and oligomeric structure of bipartite toxin YaxAB are shown as representatives of a ClyA-family bipartite toxin. YaxA (PDBID: 6EK7) is shown in violet and YaxB (PDBID: 6EK8) in green. The YaxAB pore (PDBID: 6EL1) shows a distinct overall fold from monopartite ClyA. (c) Cartoon representation of the AhlB component of the tripartite toxin AhlABC is shown in its soluble monomeric form (PDB entry 6GRK) and as an assembled pore (PDB entry 6GRJ). While the core fold of AhlB pore remains closely related to ClyA and YaxAB, there are some differences in its overall architecture. For each panel, the membrane-spanning region in the monomer, where resolved, is shown in blue.