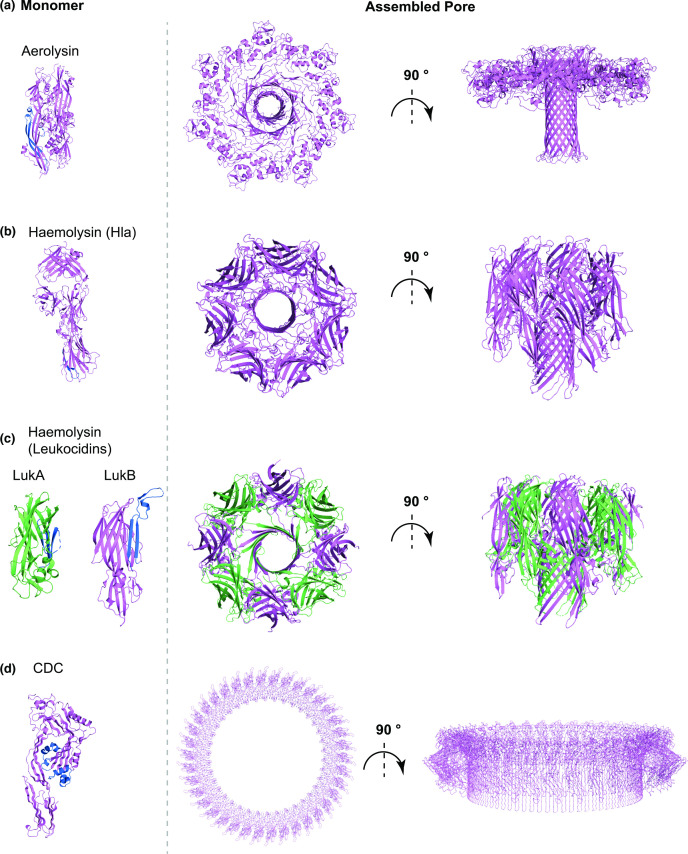
Fig. 3.
Cartoon representation of representative structures of the soluble monomer (left) and assembled pore (right) for (a) the aerolysin family, (b) the monopartite haemolysin family, (c) the bipartite haemolysin toxin family, and (d) the cholesterol-dependent cytolysin family (CDCs). (a) The aerolysin monomer (PBDID: 1PRE), shown on the left, undergoes massive rearrangements upon oligomerisation that lead to its extension and exposure of its β-barrel to the membrane. The β-barrel is then pushed into the membrane and its neighbouring region is rearranged in a rivet-like configuration for increased stability of the final pore (right, PDBID: 5JZT). (b) The Hla monomer (left, PDBID: 4IDJ) also undergoes conformational changes upon oligomerisation, similarly to aerolysin, that lead to extension of the β-barrel, which is then inserted into the membrane in the mature pore (PDBID: 7AHL). Whilst monomer extension is similar between aerolysin and Hla, the final pore structure as well as the lumen is quite different. In (c), the monomeric components LukA (PDBID: 5K59, green) and LukB (PDBID: 5K59, violet) of a bipartite leukocidin (haemolysin family) are shown on the left. Leukocidins conformation transition from soluble monomer to membrane-inserted form is similar to other haemolysins. The final assembled pore top and side views are shown on the right (PDBID: 4TW1) and it differs from Hla in terms of stoichiometry, whereas the overall 3D fold remains similar. (d) In the soluble monomer structure of perfringolysin O (left, PDBID: 1PFO) and other CDCs, the pore forming domain is organised as a β-sandwich between two a-helices. Electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy models show that in the membrane-inserted form, for each monomer, this region transitions to two amphipathic β-hairpins, which are inserted into the membrane, resulting in the final pore (biological assembly depiction from PDB entry 1PFO). For each panel, the membrane-spanning region in the monomer, where resolved, is show in blue.